Boosting of cross-reactive antibodies to endemic coronaviruses by SARS-CoV-2 infection but not vaccination with stabilized spike
- PMID: 35289271
- PMCID: PMC8923670
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.75228
Boosting of cross-reactive antibodies to endemic coronaviruses by SARS-CoV-2 infection but not vaccination with stabilized spike
Abstract
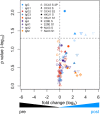
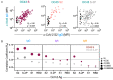
Preexisting antibodies to endemic coronaviruses (CoV) that cross-react with SARS-CoV-2 have the potential to influence the antibody response to COVID-19 vaccination and infection for better or worse. In this observational study of mucosal and systemic humoral immunity in acutely infected, convalescent, and vaccinated subjects, we tested for cross-reactivity against endemic CoV spike (S) protein at subdomain resolution. Elevated responses, particularly to the β-CoV OC43, were observed in all natural infection cohorts tested and were correlated with the response to SARS-CoV-2. The kinetics of this response and isotypes involved suggest that infection boosts preexisting antibody lineages raised against prior endemic CoV exposure that cross-react. While further research is needed to discern whether this recalled response is desirable or detrimental, the boosted antibodies principally targeted the better-conserved S2 subdomain of the viral spike and were not associated with neutralization activity. In contrast, vaccination with a stabilized spike mRNA vaccine did not robustly boost cross-reactive antibodies, suggesting differing antigenicity and immunogenicity. In sum, this study provides evidence that antibodies targeting endemic CoV are robustly boosted in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection but not to vaccination with stabilized S, and that depending on conformation or other factors, the S2 subdomain of the spike protein triggers a rapidly recalled, IgG-dominated response that lacks neutralization activity.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; conformation; epitope; human; immunology; infectious disease; inflammation; microbiology; neutralization; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
AC, HN, AH, CB, JW, WW, JL, EB, AT, AR, JB, DW, TG, AM, RC, PW, MA No competing interests declared
Figures
















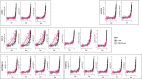
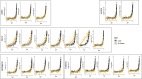




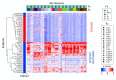




Update of
-
Boosting of Cross-Reactive Antibodies to Endemic Coronaviruses by SARS-CoV-2 Infection but not Vaccination with Stabilized Spike.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Oct 28:2021.10.27.21265574. doi: 10.1101/2021.10.27.21265574. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: Elife. 2022 Mar 15;11:e75228. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75228. PMID: 34729565 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- AckermanLab Crowley_et_al_SARS-CoV-2_Boosting. 25dbaa4GitHub. 2021 https://github.com/AckermanLab/Crowley_et_al_SARS-CoV-2_Boosting
-
- Adeniji OS, Giron LB, Purwar M, Zilberstein NF, Kulkarni AJ, Shaikh MW, Balk RA, Moy JN, Forsyth CB, Liu Q, Dweep H, Kossenkov A, Weiner DB, Keshavarzian A, Landay A, Abdel-Mohsen M. COVID-19 Severity Is Associated with Differential Antibody Fc-Mediated Innate Immune Functions. MBio. 2021;12:e00281-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00281-21. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alter G, Gorman M, Patel N, Guebre-Xabier M, Zhu A, Atyeo C, Pullen K, Loos C, Goez-Gazi Y, Carrion R, Tian J-H, Yuan D, Bowman K, Zhou B, Maciejewski S, McGrath M, Logue J, Frieman M, Montefiori D, Schendel S, Saphire EO, Lauffenburger D, Greene A, Portnoff A, Massare M, Ellingsworth L, Glenn G, Smith G, Mann C, Amanat F, Krammer F. Collaboration between the Fab and Fc contribute to maximal protection against SARS-CoV-2 following NVX-CoV2373 subunit vaccine with Matrix-M. Research Square. 2021;3:rs.3.rs-200342. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-200342/v1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amanat F, Thapa M, Lei T, Ahmed SMS, Adelsberg DC, Carreño JM, Strohmeier S, Schmitz AJ, Zafar S, Zhou JQ, Rijnink W, Alshammary H, Borcherding N, Reiche AG, Srivastava K, Sordillo EM, van Bakel H, Personalized Virology Initiative. Turner JS, Bajic G, Simon V, Ellebedy AH, Krammer F. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination induces functionally diverse antibodies to NTD, RBD, and S2. Cell. 2021;184:3936–3948. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson EM, Goodwin EC, Verma A, Arevalo CP, Bolton MJ, Weirick ME, Gouma S, McAllister CM, Christensen SR, Weaver J, Hicks P, Manzoni TB, Oniyide O, Ramage H, Mathew D, Baxter AE, Oldridge DA, Greenplate AR, Wu JE, Alanio C, D’Andrea K, Kuthuru O, Dougherty J, Pattekar A, Kim J, Han N, Apostolidis SA, Huang AC, Vella LA, Kuri-Cervantes L, Pampena MB, Betts MR, Wherry EJ, Meyer NJ, Cherry S, Bates P, Rader DJ, Hensley SE, UPenn COVID Processing Unit Seasonal human coronavirus antibodies are boosted upon SARS-CoV-2 infection but not associated with protection. Cell. 2021;184:1858–1864. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20-GM113132/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM113132/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201400008C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI120938/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI145825/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- intramural/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI120938S1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI120938/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI145825/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI128779/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23HL151826/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI120938S1/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI128779/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL151826/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

