Olaparib With or Without Cediranib Versus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Recurrent Platinum-Sensitive Ovarian Cancer (NRG-GY004): A Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trial
- PMID: 35290101
- PMCID: PMC9242406
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.02011
Olaparib With or Without Cediranib Versus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Recurrent Platinum-Sensitive Ovarian Cancer (NRG-GY004): A Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Platinum-based chemotherapy is the standard of care for platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer, but complications from repeated platinum therapy occur. We assessed the activity of two all-oral nonplatinum alternatives, olaparib or olaparib/cediranib, versus platinum-based chemotherapy.
Patients and methods: NRG-GY004 is an open-label, randomized, phase III trial conducted in the United States and Canada. Eligible patients had high-grade serous or endometrioid platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1:1 to platinum-based chemotherapy, olaparib, or olaparib/cediranib. The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS) in the intention-to-treat population. Secondary end points included activity within germline BRCA-mutated or wild-type subgroups and patient-reported outcomes (PROs).
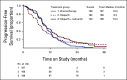
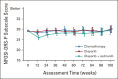
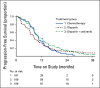
Results: Between February 04, 2016, and November 13, 2017, 565 eligible patients were randomly assigned. Median PFS was 10.3 (95% CI, 8.7 to 11.2), 8.2 (95% CI, 6.6 to 8.7), and 10.4 (95% CI, 8.5 to 12.5) months with chemotherapy, olaparib, and olaparib/cediranib, respectively. Olaparib/cediranib did not improve PFS versus chemotherapy (hazard ratio [HR] 0.86; 95% CI, 0.66 to 1.10; P = .077). In women with germline BRCA mutation, the PFS HR versus chemotherapy was 0.55 (95% CI, 0.32 to 0.94) for olaparib/cediranib and 0.63 (95% CI, 0.37 to 1.07) for olaparib. In women without a germline BRCA mutation, the PFS HR versus chemotherapy was 0.97 (95% CI, 0.73 to 1.30) for olaparib/cediranib and 1.41 (95% CI, 1.07 to 1.86) for olaparib. Hematologic adverse events occurred more commonly with chemotherapy; however, nonhematologic adverse events were higher with olaparib/cediranib. In 489 patients evaluable for PROs, patients receiving olaparib/cediranib scored on average 1.1 points worse on the NFOSI-DRS-P subscale (97.5% CI, -2.0 to -0.2, P = .0063) versus chemotherapy; no difference between olaparib and chemotherapy was observed.
Conclusion: Combination olaparib/cediranib did not improve PFS compared with chemotherapy and resulted in reduced PROs. Notably, in patients with a germline BRCA mutation, both olaparib and olaparib/cediranib had significant clinical activity.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02446600.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2021 CA Cancer J Clin 717–332021 - PubMed
-
- Caiado J, Castells M. Presentation and diagnosis of hypersensitivity to platinum drugs. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015;15:15. - PubMed
-
- Mirza MR, Avall Lundqvist E, Birrer MJ, et al. Niraparib plus bevacizumab versus niraparib alone for platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer (NSGO-AVANOVA2/ENGOT-ov24): A randomised, phase 2, superiority trial Lancet Oncol 201409–14192019 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

