Anti-Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Monoclonal Antibody Gimsilumab for COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-controlled Trial
- PMID: 35290169
- PMCID: PMC9873114
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202108-1859OC
Anti-Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Monoclonal Antibody Gimsilumab for COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-controlled Trial
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Anti-Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Monoclonal Antibody Gimsilumab for COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-controlled Trial.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Sep 15;206(6):801. doi: 10.1164/rccm.v206erratum9. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 36112778 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
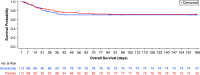
Rationale: GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor) has emerged as a promising target against the hyperactive host immune response associated with coronavirus disease (COVID-19). Objectives: We sought to investigate the efficacy and safety of gimsilumab, an anti-GM-CSF monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of hospitalized patients with elevated inflammatory markers and hypoxemia secondary to COVID-19. Methods: We conducted a 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, BREATHE (Better Respiratory Education and Treatment Help Empower), at 21 locations in the United States. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive two doses of intravenous gimsilumab or placebo 1 week apart. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality rate at Day 43. Key secondary outcomes were ventilator-free survival rate, ventilator-free days, and time to hospital discharge. Enrollment was halted early for futility based on an interim analysis. Measurements and Main Results: Of the planned 270 patients, 225 were randomized and dosed; 44.9% of patients were Hispanic or Latino. The gimsilumab and placebo groups experienced an all-cause mortality rate at Day 43 of 28.3% and 23.2%, respectively (adjusted difference = 5% vs. placebo; 95% confidence interval [-6 to 17]; P = 0.377). Overall mortality rates at 24 weeks were similar across the treatment arms. The key secondary endpoints demonstrated no significant differences between groups. Despite the high background use of corticosteroids and anticoagulants, adverse events were generally balanced between treatment groups. Conclusions: Gimsilumab did not improve mortality or other key clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and evidence of systemic inflammation. The utility of anti-GM-CSF therapy for COVID-19 remains unclear. Clinical trial registered with www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT04351243).
Keywords: COVID-19; GM-CSF; SARS-CoV-2; acute respiratory distress syndrome; gimsilumab.
Figures
Comment in
-
Less Haste, More Speed, More Science: Lessons to be Learned from COVID-19 Studies.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Jun 1;205(11):1258-1260. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202203-0617ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 35442181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA . 2020;323:1239–1242. - PubMed
-
- Liao M, Liu Y, Yuan J, Wen Y, Xu G, Zhao J, et al. Single-cell landscape of bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19. Nat Med . 2020;26:842–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous