Temporal and brain region-specific elevations of soluble Amyloid-β40-42 in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 35290711
- PMCID: PMC9009111
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13590
Temporal and brain region-specific elevations of soluble Amyloid-β40-42 in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
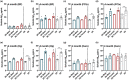
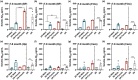
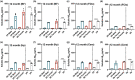
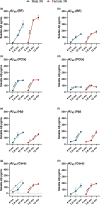
Down syndrome (DS) is a leading cause of intellectual disability that also results in hallmark Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathologies such as amyloid beta (Aβ) plaques and hyperphosphorylated tau. The Ts65Dn mouse model is commonly used to study DS, as trisomic Ts65Dn mice carry 2/3 of the triplicated gene homologues as occur in human DS. The Ts65Dn strain also allows investigation of mechanisms common to DS and AD pathology, with many of these triplicated genes implicated in AD; for example, trisomic Ts65Dn mice overproduce amyloid precursor protein (APP), which is then processed into soluble Aβ40-42 fragments. Notably, Ts65Dn mice show alterations to the basal forebrain, which parallels the loss of function in this region observed in DS and AD patients early on in disease progression. However, a complete picture of soluble Aβ40-42 accumulation in a region-, age-, and sex-specific manner has not yet been characterized in the Ts65Dn model. Here, we show that trisomic mice accumulate soluble Aβ40-42 in the basal forebrain, frontal cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum in an age-specific manner, with elevation in the frontal cortex and hippocampus as early as 4 months of age. Furthermore, we detected sex differences in accumulation of Aβ40-42 within the basal forebrain, with females having significantly higher Aβ40-42 at 7-8 months of age. Lastly, we show that APP expression in the basal forebrain and hippocampus inversely correlates with Aβ40-42 levels. This spatial and temporal characterization of soluble Aβ40-42 in the Ts65Dn model allows for further exploration of the role soluble Aβ plays in the progression of other AD-like pathologies in these key brain regions.
Keywords: Amyloid-β40-42; Ts65Dn; basal forebrain; down syndrome; hippocampus.
© 2022 The Authors. Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting increased levels of APP in Down syndrome: Posiphen-mediated reductions in APP and its products reverse endosomal phenotypes in the Ts65Dn mouse model.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Feb;17(2):271-292. doi: 10.1002/alz.12185. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 32975365 Free PMC article.
-
Normalizing the gene dosage of Dyrk1A in a mouse model of Down syndrome rescues several Alzheimer's disease phenotypes.Neurobiol Dis. 2017 Oct;106:76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.06.010. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2017. PMID: 28647555
-
Restoring microglial and astroglial homeostasis using DNA immunization in a Down Syndrome mouse model.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Jan;75:163-180. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.10.004. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 30389461 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
-
[Elucidating Pathogenic Mechanisms of Early-onset Alzheimer's Disease in Down Syndrome Patients].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017;137(7):801-805. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.16-00236-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017. PMID: 28674290 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Assessing the Benefit of Dietary Choline Supplementation Throughout Adulthood in the Ts65Dn Mouse Model of Down Syndrome.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 30;16(23):4167. doi: 10.3390/nu16234167. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683562 Free PMC article.
-
Rodent Modeling of Alzheimer's Disease in Down Syndrome: In vivo and ex vivo Approaches.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 7;16:909669. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.909669. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35747206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multisensory gamma stimulation enhances adult neurogenesis and improves cognitive function in male mice with Down Syndrome.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 24;20(4):e0317428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317428. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40273201 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pathological trajectory in the Ts65Dn model of Down syndrome.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Jan 20;15(2):295-297. doi: 10.18632/aging.204497. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 36707069 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pleiotropic effects of trisomy and pharmacologic modulation on structural, functional, molecular, and genetic systems in a Down syndrome mouse model.Elife. 2024 Mar 18;12:RP89763. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89763. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38497812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alemany‐González, M. , Gener, T. , Nebot, P. , Vilademunt, M. , Dierssen, M. , & Puig, M. V. (2020). Prefrontal‐hippocampal functional connectivity encodes recognition memory and is impaired in intellectual disability. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117, 11788–11798. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alldred, M. J. , Lee, S. H. , Stutzmann, G. E. , & Ginsberg, S. D. (2021). Oxidative phosphorylation is dysregulated within the basocortical circuit in a 6‐month old mouse model of down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 13, 707950. 10.3389/fnagi.2021.707950 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonarakis, S. E. , Lyle, R. , Dermitzakis, E. T. , Reymond, A. , & Deutsch, S. (2004). Chromosome 21 and down syndrome: from genomics to pathophysiology. Nature Reviews Genetics, 5, 725–738. - PubMed
-
- Arevalo, M.‐A. , Roldan, P. M. , Chacón, P. J. , & Rodríguez‐Tebar, A. (2009). Amyloid beta serves as an NGF‐like neurotrophic factor or acts as a NGF antagonist depending on its concentration. Journal of Neurochemistry, 111, 1425–1433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

