Uncommon case of histoplasmosis with oral manifestation: A case report of diagnosis in a South American patient
- PMID: 35290848
- PMCID: PMC8918853
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2022.106920
Uncommon case of histoplasmosis with oral manifestation: A case report of diagnosis in a South American patient
Abstract
Introduction: Histoplasmosis is a systemic fungal disease caused by the H. capsulatum fungus, which is mainly present in feces and guano of birds and bats. This condition manifests in several ways and it is more severe in its disseminated form and in immunosuppressed patients, putting the patient at risk of death if not diagnosed in time.
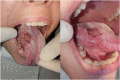
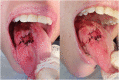
Case presentation: This report presents the case of a 39-year-old white female patient, a seller of agricultural machinery, with a history of lupus erythematosus, who attended a private dental office complaining of a tongue lesion. The patient reported having been subjected to an incisional biopsy of this lesion and the histopathological examination identified an inflammatory process. Considering the inefficient management of the lesion with intralesional application of corticosteroids, squamous cell carcinoma or granulomatous fungal infection was suspected, and a new biopsy was performed allowing the diagnosis of histoplasmosis already spread to the liver, intestines, and bone marrow. The diagnosed disease led the patient to undergo extensive antifungal treatment, including a period of hospitalization.
Discussion: The diagnosis of histoplasmosis can be delayed due to several factors, mainly due to its diverse clinical presentation between acute, chronic and disseminated forms. However, achieving an early diagnosis for histoplasmosis is very important to maintain the patient's quality of life.
Conclusion: Greater education, information, and awareness about histoplasmosis among health professionals are required for managing these cases, especially in endemic areas to H. capsulatum.
Keywords: Case report; Diagnostic; Histoplasma capsulatum; Histoplasmosis; Lupus erythematosus; Oral lesions.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors has any conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

