This is a preprint.
Low expression of EXOSC2 protects against clinical COVID-19 and impedes SARS-CoV-2 replication
- PMID: 35291294
- PMCID: PMC8923113
- DOI: 10.1101/2022.03.06.483172
Low expression of EXOSC2 protects against clinical COVID-19 and impedes SARS-CoV-2 replication
Update in
-
Low expression of EXOSC2 protects against clinical COVID-19 and impedes SARS-CoV-2 replication.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Oct 14;6(1):e202201449. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201449. Print 2023 Jan. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 36241425 Free PMC article.
Abstract
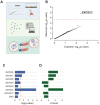
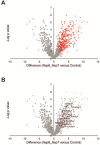
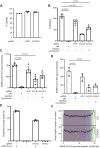
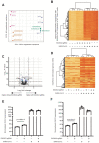
New therapeutic targets are a valuable resource in the struggle to reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified risk loci, but some loci are associated with co-morbidities and are not specific to host-virus interactions. Here, we identify and experimentally validate a link between reduced expression of EXOSC2 and reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication. EXOSC2 was one of 332 host proteins examined, all of which interact directly with SARS-CoV-2 proteins; EXOSC2 interacts with Nsp8 which forms part of the viral RNA polymerase. Lung-specific eQTLs were identified from GTEx (v7) for each of the 332 host proteins. Aggregating COVID-19 GWAS statistics for gene-specific eQTLs revealed an association between increased expression of EXOSC2 and higher risk of clinical COVID-19 which survived stringent multiple testing correction. EXOSC2 is a component of the RNA exosome and indeed, LC-MS/MS analysis of protein pulldowns demonstrated an interaction between the SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase and the majority of human RNA exosome components. CRISPR/Cas9 introduction of nonsense mutations within EXOSC2 in Calu-3 cells reduced EXOSC2 protein expression, impeded SARS-CoV-2 replication and upregulated oligoadenylate synthase ( OAS) genes, which have been linked to a successful immune response against SARS-CoV-2. Reduced EXOSC2 expression did not reduce cellular viability. OAS gene expression changes occurred independent of infection and in the absence of significant upregulation of other interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). Targeted depletion or functional inhibition of EXOSC2 may be a safe and effective strategy to protect at-risk individuals against clinical COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
M.P.S is a co-founder and member of the scientific advisory board of Personalis, Qbio, January, SensOmics, Protos, Mirvie, NiMo, Onza and Oralome. He is also on the scientific advisory board of Danaher, Genapsys and Jupiter.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low expression of EXOSC2 protects against clinical COVID-19 and impedes SARS-CoV-2 replication.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Oct 14;6(1):e202201449. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201449. Print 2023 Jan. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 36241425 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 induces double-stranded RNA-mediated innate immune responses in respiratory epithelial derived cells and cardiomyocytes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Nov 2:2020.09.24.312553. doi: 10.1101/2020.09.24.312553. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 20;118(16):e2022643118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2022643118. PMID: 32995797 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
SARS-CoV-2 pandemics: An update of CRISPR in diagnosis and host-virus interaction studies.Biomed J. 2023 Apr;46(2):100587. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.02.007. Epub 2023 Feb 25. Biomed J. 2023. PMID: 36849044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral Activity of Type I, II, and III Interferons Counterbalances ACE2 Inducibility and Restricts SARS-CoV-2.mBio. 2020 Sep 10;11(5):e01928-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01928-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32913009 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of green tea catechin, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Major interactions with host/virus proteases.Phytomed Plus. 2023 Feb;3(1):100402. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2022.100402. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Phytomed Plus. 2023. PMID: 36597465 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
