Artificial Intelligence Algorithm-Based Computed Tomography Image in Assessment of Acute Renal Insufficiency of Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- PMID: 35291424
- PMCID: PMC8901312
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2214583
Artificial Intelligence Algorithm-Based Computed Tomography Image in Assessment of Acute Renal Insufficiency of Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Abstract
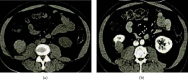
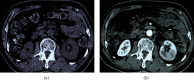
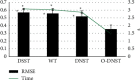
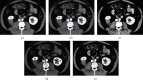
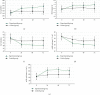
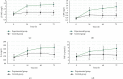
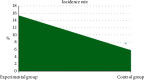
This study was aimed to analyze the changes in renal function of patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) surgery and the characteristics of their computed tomography (CT) image based on artificial intelligence algorithms. In this study, 104 patients with coronary atherosclerotic heart disease (CAHD) were treated as the research objects. They were divided into an experimental group (patients who underwent CAG and PCI within 1 week after enhanced coronary CT (ECCT)) and the control group (patients who underwent CAG and PCI within 1-3 weeks after ECCT). Renal imaging scans of patients were performed by CT based on discrete inseparable shear transform (DNST) optimized algorithm, which was named as O-DNST. The results showed that the serum creatinine (Scr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and urine protein (UP) levels of patients in the experimental group were significantly higher than those of the control group 24-72 hours after surgery, while the levels of endogenous creatinine clearance (Ccr) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were significantly lower than those of the control group (P < 0.05). The levels of β2 microglobulin (β2-MG), C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) in the experimental group were significantly higher than those in the control group 24-72 hours after surgery (P < 0.05). The incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) in the experimental group (15.38%) was significantly higher than that in the control group (5.8%), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The results showed that repeated application of contrast agent in a short period of time can promote the increase of serum inflammation levels in PCI patients, which may be a risk factor for CIN in PCI patients.
Copyright © 2022 Xiuming Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effect of probucol on preventing contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Nov 7;97(41):3234-3238. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.41.008. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29141361 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effect of Alprostadil on the Prevention of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy: A Meta-Analysis of 36 Randomized Controlled Trials.Angiology. 2019 Aug;70(7):594-612. doi: 10.1177/0003319719825597. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Angiology. 2019. PMID: 30669852 Review.
-
Analysis of the risk factors for contrast-induced nephropathy in over-aged patients receiving coronary intervention.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Aug;243(12):970-975. doi: 10.1177/1535370218799973. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 30299175 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of probucol combined with hydration in preventing contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with coronary heart disease undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a multicenter, prospective, randomized controlled study.Int Urol Nephrol. 2018 Jan;50(1):105-112. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1718-4. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29071556 Clinical Trial.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning reduces the incidence of contrast-induced nephropathy in patients undergoing coronary angiography/intervention: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020 Nov;96(6):1200-1212. doi: 10.1002/ccd.28709. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020. PMID: 31912996
Cited by
-
Predictive performance of machine learning models for kidney complications following coronary interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Mar;57(3):855-874. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04257-5. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39477885
References
-
- Chen Y., Hu S., Mao H., Deng W., Gao X. Application of the best evacuation model of deep learning in the design of public structures. Image and Vision Computing . 2020;102 doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2020.103975.103975 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
