Effect of Preoperative Administration of Oral Melatonin on Pneumatic Tourniquet-Induced Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Orthopedic Surgery of Lower Extremities: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 35291433
- PMCID: PMC8919302
- DOI: 10.30476/ijms.2021.86960.1701
Effect of Preoperative Administration of Oral Melatonin on Pneumatic Tourniquet-Induced Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Orthopedic Surgery of Lower Extremities: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Ischemic reperfusion injury (IRI) causes cellular damage and dysfunction. The present study aimed to evaluate the effect of melatonin on pneumatic tourniquet-induced IRI in orthopedic surgery of the lower extremities.
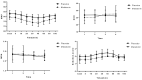
Methods: A randomized clinical trial was conducted at Chamran Hospital, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (Shiraz, Iran), from September to November 2019. The target population was patients scheduled for elective orthopedic surgery of the lower extremities. A total of 67 patients were randomly divided into two groups, placebo (n=34) and melatonin (n=33). The groups received 10 mg melatonin or placebo the night before surgery and two hours before surgery. Primary outcome variables were the serum levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA). Hemodynamic parameters, sedation score, and drug side effects were also evaluated. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 21.0 software. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: In the analysis phase, due to loss to follow-up (n=26), 41 patients divided into two groups of melatonin (n=20) and placebo (n=21) were evaluated. There was no significant difference in demographic data, duration of surgery (P=0.929), and tourniquet time (P=0.496) between the groups. The serum levels of SOD and MDA were not significantly different between the groups (P=0.866 and P=0.422, respectively), nor were the incidence of postoperative nausea (P=0.588) and patients' satisfaction (P=0.088). However, the postoperative sedation score and vomiting between the groups were significantly different (P<0.001).
Conclusion: Administration of 10 mg melatonin provided effective sedation, but had no significant effect on the serum levels of SOD and MDA, nor on pneumatic tourniquet-induced IRI in orthopedic surgery of the lower limbs.
Trial registration number: IRCT20141009019470N87.
Keywords: Malondialdehyde; Melatonin; Reperfusion injury; Superoxide dismutase.
Copyright: © Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Sharma JP, Salhotra R. Tourniquets in orthopedic surgery. Indian J Orthop. 2012;46:377–83. doi: 10.4103/0019-5413.98824. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haimovici H. Metabolic complications of acute arterial occlusions and skeletal muscle ischemia: myonephropatic metabolic syndrome. Haimovici’s Vascular Surgery Principal and Techniques. 1996
-
- Tibrewal SB. The pneumatic tourniquet in arthroscopic surgery of the knee. Int Orthop. 2001;24:347–9. doi: 10.1007/s002640000180. [ PMC Free Article ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saritas T, Buyukbas S, Peker K, Borazan H, Basarali K. The Effect of Oral Melatonin Premedication on Pneumatic Tourniquet Induced Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Lower Extremity Operations. J Pain Relief. 2015;4:2. doi: 10.4172/2167-0846.1000208. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources