A versatile isothermal amplification assay for the detection of leptospires from various sample types
- PMID: 35291487
- PMCID: PMC8918162
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12850
A versatile isothermal amplification assay for the detection of leptospires from various sample types
Abstract
Background: Leptospirosis is a zoonotic disease caused by bacteria of the genus Leptospira that affects both humans and animals worldwide. Early detection of the pathogen in humans is crucial for early intervention and control of the progression of the disease to a severe state. It is also vitally important to be able to detect the presence of the pathogen in carrier animals to control the spread of the disease from the environment. Here we developed a simple and rapid loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay targeting the leptospiral secY gene.
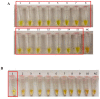
Results: Several reaction conditions of the LAMP reaction were optimized to ensure efficient amplification of the target DNA. The sensitivity of the developed LAMP assay obtained using a pure Leptospira culture was 2 × 104 copies of genomic DNA per reaction (equivalent to 0.1 ng) for a 40-minute reaction time. No cross-reactions were observed in the LAMP reaction against a series of non-leptospiral bacteria, indicating a specific reaction. The applicability of the LAMP assay was demonstrated on human blood and urine specimens collected from suspected leptospirosis patients and rat kidney specimens collected from suspected leptospirosis outbreak areas and high-risk areas. The developed LAMP assay demonstrated a higher detection rate for leptospiral DNA compared with the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay, possibly due to the presence of inhibitory substances, especially in rat kidney specimens, to which the PCR method is more susceptible. The present findings also highlight the importance of urine sample collection from patients for routine monitoring of the disease.
Conclusions: In short, the developed LAMP assay can serve as a feasible alternative tool for the diagnosis of leptospirosis and be used for epidemiological and environmental surveillance of the disease, considering its robustness, rapidity, sensitivity, and specificity, as demonstrated in this study.
Keywords: Clinical detection; Loop-mediated isothermal amplification; Vector surveillance; Leptospirosis.
©2022 Othman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Shuhaidah Othman, Jia Yong Lam, and Hui Yee Chee have patented a method for detecting Leptospira with the patent no: PI2019002320. All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Optimization and comparative analysis of LAMP and PCR techniques for the detection of leptospiral DNA in Golden Syrian hamsters.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Feb;48(1):103-111. doi: 10.1007/s11259-023-10183-1. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 37540477
-
Application of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for the detection of pathogenic Leptospira.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009 Mar;63(3):237-42. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2008.10.012. Epub 2008 Dec 12. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19070450
-
Evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification method (LAMP) for pathogenic Leptospira spp. detection with leptospires isolation and real-time PCR.J Vet Med Sci. 2016 Sep 1;78(8):1299-302. doi: 10.1292/jvms.15-0702. Epub 2016 May 6. J Vet Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27150208 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleic acid and antigen detection tests for leptospirosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Aug 1;8(8):CD011871. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011871.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31425612 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of diagnostic accuracy of loop-mediated isothermal amplification method (LAMP) compared with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for Leptospira spp. in clinical samples: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021 Jul;100(3):115369. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2021.115369. Epub 2021 Mar 13. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33845305
Cited by
-
Can Wastewater Surveillance Enhance Genomic Tracking of Climate-Driven Pathogens?Microorganisms. 2025 Jan 28;13(2):294. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020294. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection of Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia spp. in Environmental Water Samples: A Journey into the Past and New Perspectives.Microorganisms. 2022 Jun 7;10(6):1175. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061175. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35744692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ketone body oxidation and susceptibility to ethyl acetoacetate in a novel hemolytic multidrug-resistant strain Leptospira interrogans KeTo originated from sewage water.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 24;14(1):25198. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76546-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39448678 Free PMC article.
-
Leptospirosis-Improving Healthcare Outcomes for a Neglected Tropical Disease.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025 Feb 10;12(2):ofaf035. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf035. eCollection 2025 Feb. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39963696 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdullahi UF, Naim R, Taib WRW, Saleh A, azu AMu, Aliyu S, Baig AA. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), an innovation in gene amplification: bridging the gap in molecular diagnostics; a review. Indian Journal of Science and Technology. 2015;8(17):1–12.
-
- Adler B. History of leptospirosis and leptospira. In: Adler B, editor. Leptospira and leptospirosis. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; Berlin, Heidelberg: 2015. pp. 1–9.
-
- Ahmad SN, Shah S, Ahmad FM. Laboratory diagnosis of leptospirosis. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine. 2005;51:195–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

