Targeting the Epithelium-Derived Innate Cytokines: From Bench to Bedside
- PMID: 35291657
- PMCID: PMC8901708
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e11
Targeting the Epithelium-Derived Innate Cytokines: From Bench to Bedside
Abstract
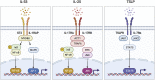
When epithelial cells are exposed to potentially threatening external stimuli such as allergens, bacteria, viruses, and helminths, they instantly produce "alarmin" cytokines, namely, IL-33, IL-25, and TSLP. These alarmins alert the immune system about these threats, thereby mobilizing host immune defense mechanisms. Specifically, the alarmins strongly stimulate type-2 immune cells, including eosinophils, mast cells, dendritic cells, type-2 helper T cells, and type-2 innate lymphoid cells. Given that the alarm-raising role of IL-33, IL-25, and TSLP was first detected in allergic and infectious diseases, most studies on alarmins focus on their role in these diseases. However, recent studies suggest that alarmins also have a broad range of effector functions in other pathological conditions, including psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, and cancer. Therefore, this review provides an update on the epithelium-derived cytokines in both allergic and non-allergic diseases. We also review the progress of clinical trials on biological agents that target the alarmins and discuss the therapeutic potential of these agents in non-allergic diseases.
Keywords: Alarmins; Autoimmune disease; Biological therapy; Hypersensitivity.
Copyright © 2022. The Korean Association of Immunologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epithelial cell alarmin cytokines: Frontline mediators of the asthma inflammatory response.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 14;13:975914. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.975914. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting alarmins in asthma: From bench to clinic.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025 Apr;155(4):1133-1148. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2025.01.017. Epub 2025 Jan 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39855362 Review.
-
The Role of Airway Epithelial Cell Alarmins in Asthma.Cells. 2022 Mar 24;11(7):1105. doi: 10.3390/cells11071105. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Alarmins: A New Perspective for Biological Therapies of Severe Asthma.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 29;9(9):1108. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091108. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial cell-derived cytokines: more than just signaling the alarm.J Clin Invest. 2019 Apr 1;129(4):1441-1451. doi: 10.1172/JCI124606. Epub 2019 Apr 1. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30932910 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Esophageal ILC2s mediate abnormal epithelial remodeling in eosinophilic esophagitis via Areg-EGFR signaling.Cell Mol Immunol. 2025 Jan;22(1):97-110. doi: 10.1038/s41423-024-01242-x. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Cell Mol Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39653767 Free PMC article.
-
A Dynamic Interplay of Innate Immune Responses During Urinary Tract Infection.Immune Netw. 2024 Jul 22;24(4):e31. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e31. eCollection 2024 Aug. Immune Netw. 2024. PMID: 39246616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential roles of interleukin-25 in infectious diseases.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 2;13:986118. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.986118. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-18 Binding Protein (IL-18BP): A Long Journey From Discovery to Clinical Application.Immune Netw. 2024 Jan 15;24(1):e1. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e1. eCollection 2024 Feb. Immune Netw. 2024. PMID: 38455460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Golden Age of Immunotherapy: Challenges and Opportunities.Immune Netw. 2022 Feb 21;22(1):e1. doi: 10.4110/in.2022.22.e1. eCollection 2022 Feb. Immune Netw. 2022. PMID: 35291654 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hammad H, Lambrecht BN. Barrier epithelial cells and the control of type 2 immunity. Immunity. 2015;43:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Oppenheim JJ, Yang D. Alarmins: chemotactic activators of immune responses. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17:359–365. - PubMed
-
- Gamez C, Metcalfe J, Prescott SL, Palmer DJ. Lower cord blood IL-17 and IL-25, but not other epithelial cell-derived cytokines are associated with atopic dermatitis in infancy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2021;182:474–478. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

