circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury
- PMID: 35291714
- PMCID: PMC8886607
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2022-0417
circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury
Retraction in
-
Retraction of "circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury".Open Med (Wars). 2023 Dec 31;18(1):20230891. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0891. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 38196809 Free PMC article.
Abstract
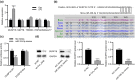
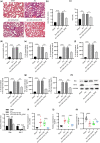
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a respiratory disorder characterized by acute respiratory failure. circRNA mus musculus (mmu)-circ_0001679 was reported overexpressed in septic mouse models of ALI. Here the function of circ_0001679 in sepsis-induced ALI was investigated. In vitro models and animal models with ALI were, respectively, established in mouse lung epithelial (MLE)-12 cells and C57BL/6 mice. Pulmonary specimens were harvested for examination of the pathological changes. The pulmonary permeability was examined by wet-dry weight (W/D) ratio and lung permeability index. The levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), the lung tissues, and the supernatant of MLE-12 cells were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay . Apoptosis was determined by flow cytometry. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay were used to assess the interactions between genes. We found that circ_0001679 was overexpressed in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated MLE-12 cells. circ_0001679 knockdown suppressed apoptosis and proinflammatory cytokine production induced by LPS. Moreover, circ_0001679 bound to mmu-miR-338-3p and miR-338-3p targeted dual-specificity phosphatases 16 (DUSP16). DUSP16 overexpression reversed the effect of circ_0001679 knockdown in LPS-stimulated MLE-12 cells. Furthermore, circ_0001679 knockdown attenuated lung pathological changes, reduced pulmonary microvascular permeability, and suppressed inflammation in ALI mice. Overall, circ_0001679 knockdown inhibits sepsis-induced ALI progression through the miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis.
Keywords: DUSP16; circ_0001679; miR-338-3p; sepsis.
© 2022 Jiang Zhu et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that there exists no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Knockdown of circ_0001679 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced MLE-12 lung cell injury by regulating the miR-338-3p/ mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):5803-5817. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2034564. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35264058 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing circPalm2 inhibits sepsis-induced acute lung injury by sponging miR-376b-3p and targeting MAP3K1.Toxicol Res. 2023 Jan 17;39(2):275-294. doi: 10.1007/s43188-022-00169-7. eCollection 2023 Apr. Toxicol Res. 2023. PMID: 37008689 Free PMC article.
-
Calycosin Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice through the miR-375-3p/ROCK2 Axis.J Invest Surg. 2023 Dec;36(1):2211166. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2023.2211166. J Invest Surg. 2023. PMID: 37400250
-
Circ-BNIP3L knockdown alleviates LPS-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury during sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by miR-370-3p/MYD88 axis.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2021 Dec;53(6):665-677. doi: 10.1007/s10863-021-09925-0. Epub 2021 Nov 3. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2021. PMID: 34731384
-
Circ_0114428 Regulates Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury by Targeting the miR-495-3p/CRBN Axis.Inflammation. 2021 Aug;44(4):1464-1477. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01432-z. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33830389
Cited by
-
Circular RNAs in organ injury: recent development.J Transl Med. 2022 Nov 18;20(1):533. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03725-9. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36401311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA protein tyrosine kinase 2 aggravates pyroptosis and inflammation in septic lung tissue by promoting microRNA-766/eukaryotic initiation factor 5A axis-mediated ATP efflux.Acta Cir Bras. 2023 Mar 6;38:e380323. doi: 10.1590/acb380323. eCollection 2023. Acta Cir Bras. 2023. PMID: 36888755 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0114428 knockdown inhibits ROCK2 expression to assuage lipopolysaccharide-induced human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cell injury through miR-574-5p.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Jan 31;74(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12576-023-00891-3. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38297223 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of circular RNAs in lung injury.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 27;15:1354806. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1354806. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38601461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNA-338-3p Inhibits Neuroinflammation in the Corpus Callosum of LCV-LPS Rats Via STAT1 Signal Pathway.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;43(7):3669-3692. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01378-w. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37479855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee J, Levy MM. Treatment of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: current evidence-based practices. Rhode Isl Med J (2013). 2019;102(10):18–21. - PubMed
- Lee J, Levy MM. Treatment of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: current evidence-based practices. Rhode Isl Med J (2013) 2019;102(10):18–21. - PubMed
-
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). Jama. 2016;315(8):801–10. - PMC - PubMed
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M. et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3) Jama. 2016;315(8):801–10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sevransky JE, Martin GS, Shanholtz C, Mendez-Tellez PA, Pronovost P, Brower R, et al. Mortality in sepsis versus non-sepsis induced acute lung injury. Crit Care (London, Engl). 2009;13(5):R150. - PMC - PubMed
- Sevransky JE, Martin GS, Shanholtz C, Mendez-Tellez PA, Pronovost P, Brower R. et al. Mortality in sepsis versus non-sepsis induced acute lung injury. Crit Care (London, Engl) 2009;13(5):R150. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hernu R, Wallet F, Thiollière F, Martin O, Richard JC, Schmitt Z, et al. An attempt to validate the modification of the American-European consensus definition of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome by the Berlin definition in a university hospital. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39(12):2161–70. - PubMed
- Hernu R, Wallet F, Thiollière F, Martin O, Richard JC, Schmitt Z. et al. An attempt to validate the modification of the American-European consensus definition of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome by the Berlin definition in a university hospital. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39(12):2161–70. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
