Mendelian randomization study of circulating lipids and biliary tract cancer among East Asians
- PMID: 35291981
- PMCID: PMC8922750
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09382-x
Mendelian randomization study of circulating lipids and biliary tract cancer among East Asians
Abstract
Background: Associations of High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, total cholesterol (CHL), and triglyceride (TRG) concentrations with risk of biliary tract cancer (BtC) were conflicting in observational studies. We aim to investigate the causal link between circulating lipids and BtC using genetic information.
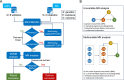
Methods: Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the four circulating lipids (n = 34,421) and BtC (418 cases and 159,201 controls) were retrieved from two independent GWAS studies performed in East Asian populations. Two-sample univariate and multivariate Mendelian Randomization (MR) analyses were conducted to determine the causal link between circulating lipids and BtC.
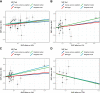
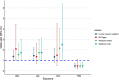
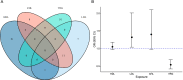
Results: No significant horizontal pleiotropy was detected for all circulating lipids according to the MR-PRESSO global test (P = 0.458, 0.368, 0.522, and 0.587 for HDL, LDL, CHL, and TRG, respectively). No significant evidence of heterogeneity and directional pleiotropy was detected by the Cochran's Q test and MR-Egger regression. Univariate MR estimates from inverse variance weighting method suggested that one standard deviation (1-SD) increase of inverse-normal transformed HDL (OR = 1.38, 95% CI 0.98-1.94), LDL (OR = 1.46, 95% CI 0.96-2.23), and CHL (OR = 1.34, 95% CI 0.83-2.16) were not significantly associated with BtC risk. Whereas 1-SD increase of inverse-normal transformed TRG showed a significantly negative association with BtC risk (OR = 0.48, 95% CI 0.31-0.74). In multivariate MR analyses including all the four lipid traits, we found that 1-SD increase of LDL and TRG was significantly associated with elevated (OR = 1.32, 95% CI 1.04-2.01) and decreased (OR = 0.54, 95% CI 0.42-0.68) risk of BtC, respectively.
Conclusion: Circulating lipids, particularly LDL and TRG, may have roles in the development of BtC. However, the results of this study should be replicated in MR with larger GWAS sample sizes for BtC.
Keywords: Biliary tract cancer; Cholesterol; HDL; LDL; Lipid; Mendelian randomization; Triglyceride.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Colombet M, Mery L, Piñeros M, Znaor A, Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2020.
-
- Lowenfels AB, Lindström CG, Conway MJ, Hastings PR. Gallstones and risk of gallbladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985;75(1):77–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

