LncRNA-mediated DNA methylation: an emerging mechanism in cancer and beyond
- PMID: 35292092
- PMCID: PMC8922926
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-022-02319-z
LncRNA-mediated DNA methylation: an emerging mechanism in cancer and beyond
Erratum in
-
Correction: LncRNA-mediated DNA methylation: an emerging mechanism in cancer and beyond.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Aug 27;41(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02468-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36028910 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
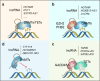
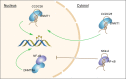
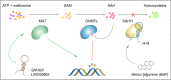
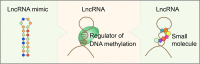
DNA methylation is one of the most important epigenetic mechanisms to regulate gene expression, which is highly dynamic during development and specifically maintained in somatic cells. Aberrant DNA methylation patterns are strongly associated with human diseases including cancer. How are the cell-specific DNA methylation patterns established or disturbed is a pivotal question in developmental biology and cancer epigenetics. Currently, compelling evidence has emerged that long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) mediates DNA methylation in both physiological and pathological conditions. In this review, we provide an overview of the current understanding of lncRNA-mediated DNA methylation, with emphasis on the roles of this mechanism in cancer, which to the best of our knowledge, has not been systematically summarized. In addition, we also discuss the potential clinical applications of this mechanism in RNA-targeting drug development.
Keywords: Cancer; DNA methylation; DNMT; Non-coding RNA; TET; lncRNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA epigenetics in pulmonary diseases: Insights into methylation modification of lncRNAs in lung cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jun;175:116704. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116704. Epub 2024 May 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38749181 Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA, the methylation of genomic elements and their emerging crosstalk in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2016 Sep 1;379(2):239-44. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.08.008. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26282784 Review.
-
DNA methylation of HOX genes and its clinical implications in cancer.Exp Mol Pathol. 2023 Dec;134:104871. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2023.104871. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Exp Mol Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37696326 Review.
-
Pan-cancer analysis of the DNA methylation patterns of long non-coding RNA.Genomics. 2022 Jul;114(4):110377. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110377. Epub 2022 May 2. Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35513292
-
The interaction between DNA methylation and long non-coding RNA during the onset of puberty in goats.Reprod Domest Anim. 2018 Dec;53(6):1287-1297. doi: 10.1111/rda.13246. Epub 2018 Jul 7. Reprod Domest Anim. 2018. PMID: 29981216
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of CPNE1 predicts prognosis and drug resistance in gastric adenocarcinoma.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Jun 15;16(6):2233-2247. doi: 10.62347/NIYR2094. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39006290 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation of miR-181a-5p mediated by DNMT3b drives renal interstitial fibrosis developed from acute kidney injury.Epigenomics. 2024;16(13):945-960. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2024.2370229. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Epigenomics. 2024. PMID: 39023272 Free PMC article.
-
The study of the mechanism of non-coding RNA regulation of programmed cell death in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Jul;479(7):1673-1696. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04909-7. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38189880 Review.
-
LncRNA FOXD2-AS1 Increased Proliferation and Invasion of Lung Adenocarcinoma via Cell-Cycle Regulation.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023 Feb 3;16:99-109. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S396866. eCollection 2023. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36761100 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs in skin cancers:Biological roles and molecular mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 10;13:934396. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.934396. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36034860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

