[Comparison of locking plate and intramedullary nail in treatment of Neer two- and three-part fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly]
- PMID: 35293166
- PMCID: PMC8923928
- DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.202107003
[Comparison of locking plate and intramedullary nail in treatment of Neer two- and three-part fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly]
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effectiveness of locking plate and intramedullary nail in treatment of Neer two- and three-part fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly.
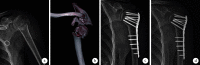
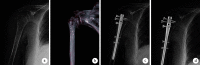
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 86 elderly patients with Neer two- and three-part fractures of the proximal humerus met the selection criteria between January 2015 and December 2018. Forty-six patients were treated with locking plate fixation (locking plate group), and 40 patients with intramedullary nail fixation (intramedullary nail group). There was no significant difference in gender, age, cause of injury, fracture side and type, time from injury to operation, and comorbidities between the two groups ( P>0.05). Visual analogue scale (VAS) score, American Shoulder and Elbow Surgery (ASES) score, Constant-Murley score, and shoulder range of motion (forward flexion, abduction, and external rotation) were compared between the two groups. X-ray films were taken to assess the fracture healing, and the neck-shaft angle was measured at 2 days after operation and at last follow-up, and the difference between the two time points was calculated.
Results: Patients in both groups were followed up 18-40 months, with an average of 30.4 months. There was no significant difference in follow-up time between the two groups ( t=-0.986, P=0.327). X-ray films reexamination showed that the fractures of two groups healed, and the healing time was (11.3±2.1) weeks in locking plate group and (10.3±2.0) weeks in intramedullary nail group, which had significant difference between the two groups ( t=2.250, P=0.027). The difference of neck-shaft angle was (7.63±7.01)° in locking plate group and (2.85±2.82)° in intramedullary nail group, which had significant difference between the two groups ( t=4.032, P<0.001). There was no significant difference in Constant-Murley score, ASES score, VAS score, and shoulder range of motion between the two groups at last follow-up ( P>0.05). Complications occurred in 13 cases (28.3%) of locking plate group and in 4 cases (10.0%) of intramedullary nail group, and the difference between the two groups was significant ( χ 2=4.498, P=0.034).
Conclusion: Both locking plates and intramedullary nails can be used for the treatment of Neer two- and three-part fractures of the proximal humerus in the elderly. The intramedullary nail fixation surgery is more minimally invasive, which has fewer postoperative complications and faster fracture healing.
目的: 比较锁定钢板及髓内钉治疗老年肱骨近端Neer二、三部分骨折的疗效。.
方法: 回顾分析2015年1月—2018年12月符合选择标准的86例肱骨近端Neer二、三部分骨折老年患者临床资料。其中,46例行锁定钢板固定(锁定钢板组),40例行髓内钉固定(髓内钉)。两组患者性别、年龄、致伤原因、骨折侧别及分型、受伤至手术时间以及合并损伤等一般资料比较,差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。比较两组疼痛视觉模拟评分(VAS)、美国肩肘外科(ASES)评分、Constant-Murley评分,以及肩关节活动度(前屈、外展、外旋);X线片复查骨折愈合情况,于术后第2天及末次随访图像测量颈干角并计算差值。.
结果: 两组患者均获随访,随访时间18~40个月,平均30.4个月;两组随访时间差异无统计学意义( t=−0.986, P=0.327)。X线片复查示两组骨折均愈合,锁定钢板组骨折愈合时间为(11.3±2.1)周,髓内钉组为(10.3±2.0)周,差异有统计学意义( t=2.250, P=0.027)。锁定钢板组颈干角差值为(7.63±7.01)°,髓内钉组为(2.85±2.82)°,差异有统计学意义( t=4.032, P<0.001)。末次随访时,两组Constant-Murley评分、ASES评分、VAS评分及肩关节活动度比较,差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。锁定钢板组13例(28.3%)、髓内钉组4例(10.0%)发生并发症,差异有统计学意义( χ 2=4.498, P=0.034)。.
结论: 锁定钢板及髓内钉均可用于治疗老年肱骨近端Neer二、三部分骨折,其中髓内钉固定手术更加微创,术后并发症更少,骨折愈合更快。.
Keywords: Proximal humeral fracture; internal fixation; intramedullary nail; locking plate; the elderly.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突 所有作者声明,在课题研究和文章撰写过程中不存在利益冲突
Figures
References
-
-
Tepass A, Rolauffs B, Weise K, et al. Complication rates and outcomes stratified by treatment modalities in proximal humeral fractures: a systematic literature review from 1970-2009. Patient Saf Surg, 2013, 7(1): 34. doi: 10.1186/1754-9493-7-34.
-
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous