CLEC5a-directed bispecific antibody for effective cellular phagocytosis
- PMID: 35293277
- PMCID: PMC8932924
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2022.2040083
CLEC5a-directed bispecific antibody for effective cellular phagocytosis
Abstract
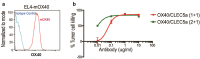
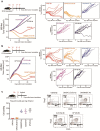
While antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis mediated by activating Fcγ receptor is a key mechanism underlying many antibody drugs, their full therapeutic activities can be restricted by the inhibitory Fcγ receptor IIB (FcγRIIB). Here, we describe a bispecific antibody approach that harnesses phagocytic receptor CLEC5A (C-type Lectin Domain Containing 5A) to drive Fcγ receptor-independent phagocytosis, potentially circumventing the negative impact of FcγRIIB. First, we established the effectiveness of such an approach by constructing bispecific antibodies that simultaneously target CLEC5A and live B cells. Furthermore, we demonstrated its in vivo application for regulatory T cell depletion and subsequent tumor regression.
Keywords: CLEC5A; Fcγ receptor; Phagocytosis; bispecific antibody; treg; tumor-associated macrophage.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
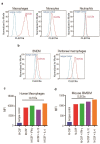
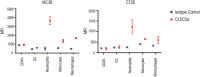
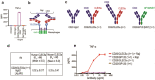

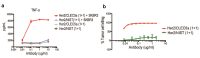

References
-
- Overdijk MB, Verploegen S, Bögels M, van Egmond M, Lammerts Van Bueren JJ, Mutis T, Groen RWJ, Breij E, Martens ACM, Bleeker WK, et al. Antibody-mediated phagocytosis contributes to the anti-tumor activity of the therapeutic antibody daratumumab in lymphoma and multiple myeloma. mAbs. 2015;7(2):311–12. doi:10.1080/19420862.2015.1007813. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Fan X, Deng H, Brezski RJ, Rycyzyn M, Jordan RE, Strohl WR, Zou Q, Zhang N, An Z. Trastuzumab triggers phagocytic killing of high her2 cancer cells in vitro and in vivo by interaction with Fcγ receptors on macrophages. J Immunol. 2015;194(9):4379–86. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1402891. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
