Decision uncertainty during hypothesis testing enhances memory accuracy for incidental information
- PMID: 35293323
- PMCID: PMC8973392
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.053458.121
Decision uncertainty during hypothesis testing enhances memory accuracy for incidental information
Abstract
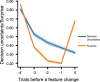
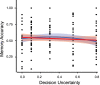
Humans actively seek information to reduce uncertainty, providing insight on how our decisions causally affect the world. While we know that episodic memories can help support future goal-oriented behaviors, little is known about how hypothesis testing during exploration influences episodic memory. To investigate this question, we designed a hypothesis testing paradigm, in which participants figured out rules to unlock treasure chests. Using this paradigm, we characterized how hypothesis testing during exploration influenced memory for the contents of the treasure chests. We found that there was an inverted U-shaped relationship between decision uncertainty and memory, such that memory was best when decision uncertainty was moderate. An exploratory analysis also showed that surprising outcomes lead to lower memory confidence independent of accuracy. These findings support a model in which moderate decision uncertainty during hypothesis testing enhances incidental information encoding.
© 2022 Shen et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures
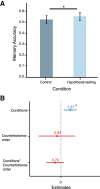
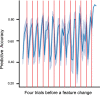
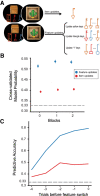
References
-
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S. 2015. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67: 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
-
- Gottlieb J, Lopes M, Oudeyer P-Y. 2016. Motivated cognition: neural and computational mechanisms of curiosity, attention, and intrinsic motivation. In Advances in motivation and achievement (ed. Kim S et al. ), vol. 19, pp. 149–172. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, Bradford, West Yorkshire, England.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
