Extracellular matrix proteins regulate NK cell function in peripheral tissues
- PMID: 35294229
- PMCID: PMC8926340
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abk3327
Extracellular matrix proteins regulate NK cell function in peripheral tissues
Abstract
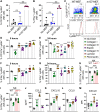
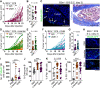
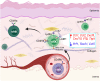
Natural killer (NK) cells reject major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I)-deficient bone marrow through direct cytotoxicity but not solid organ transplants devoid of MHC-I. Here, we demonstrate an immediate switch in NK cell function upon exit from the circulation, characterized by a shift from direct cytotoxicity to chemokine/cytokine production. In the skin transplant paradigm, combining an NK cell-specific activating ligand, m157, with missing self MHC-I resulted in complete graft rejection, which was dependent on NK cells as potential helpers and T cells as effectors. Extracellular matrix proteins, collagen I, collagen III, and elastin, blocked NK cell cytotoxicity and promoted their chemokine/cytokine production. NK cell cytotoxicity against MHC-I-deficient melanoma in the skin was markedly increased by blocking tumor collagen deposition. MHC-I down-regulation occurred in solid human cancers but not leukemias, which could be directly targeted by circulating cytotoxic NK cells. Our findings uncover a fundamental mechanism that restricts direct NK cell cytotoxicity in peripheral tissues.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HLA class I, NKG2D, and natural cytotoxicity receptors regulate multiple myeloma cell recognition by natural killer cells.Blood. 2005 Jan 1;105(1):251-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1422. Epub 2004 Aug 24. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15328155
-
Renal allograft rejection: protection of renal epithelium from natural killer cells by cytokine-induced up-regulation of class I major histocompatibility antigens.Immunology. 1993 Jun;79(2):290-7. Immunology. 1993. PMID: 8344707 Free PMC article.
-
Lysis of pig endothelium by IL-2 activated human natural killer cells is inhibited by swine and human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I gene products.Ann Transplant. 1997;2(1):14-20. Ann Transplant. 1997. PMID: 9869836
-
Dual effects of cytokines in regulation of MHC-unrestricted cell mediated cytotoxicity.Crit Rev Immunol. 1993;13(1):1-34. Crit Rev Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8466640 Review.
-
Enhancing Natural Killer and CD8+ T Cell-Mediated Anticancer Cytotoxicity and Proliferation of CD8+ T Cells with HLA-E Monospecific Monoclonal Antibodies.Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2019 Apr;38(2):38-59. doi: 10.1089/mab.2018.0043. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2019. PMID: 31009335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current status and perspective of tumor immunotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 26;10:941750. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.941750. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36092724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in oncolytic virus combined immunotherapy in tumor treatment.Genes Dis. 2025 Mar 12;12(6):101599. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2025.101599. eCollection 2025 Nov. Genes Dis. 2025. PMID: 40821119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unleashing NK cells for cancer immunotherapy in lung cancer: biologic challenges and clinical advances.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Aug 23;44(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03503-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40849493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutics to harness the immune microenvironment in multiple myeloma.Cancer Drug Resist. 2022 Jun 22;5(3):647-661. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2022.23. eCollection 2022. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36176763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cell activity in the tumor microenvironment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 30;13:1609479. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1609479. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40519272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Karlhofer F. M., Ribaudo R. K., Yokoyama W. M., MHC class I alloantigen specificity of Ly-49+ IL-2-activated natural killer cells. Nature 358, 66–70 (1992). - PubMed
-
- Bennett M., Yu Y. Y., Stoneman E., Rembecki R. M., Mathew P. A., Lindahl K. F., Kumar V., Hybrid resistance: ‘Negative’ and ‘positive’ signaling of murine natural killer cells. Semin. Immunol. 7, 121–127 (1995). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

