Diuretics: a contemporary pharmacological classification?
- PMID: 35294605
- PMCID: PMC9072265
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-022-02228-0
Diuretics: a contemporary pharmacological classification?
Abstract
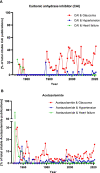
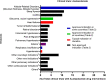
Diuretics are drugs that increase the flow of urine. They are commonly used to treat edema, hypertension, and heart failure. Typically, the pharmacological group consists of five classes: thiazide diuretics, loop diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, osmotic diuretics, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. This traditional classification and the nomenclature of diuretics have not changed over the last decades, which means that it was not adapted to current pharmacological research. Modern approaches in the field of pharmacological nomenclature suggest the introduction of mechanism-based drug class designations, which is not yet reflected in the group of diuretics. Moreover, included drug classes have lost their relevance as diuretic agents. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, for example, are mainly used in the treatment of glaucoma. Newer agents such as vasopressin-2 receptor antagonists or SGLT2 inhibitors possess diuretic properties but are not included in the pharmacological group. This review discusses the currentness of the pharmacological classification of diuretics. We elaborate changes in the field of nomenclature, the contemporary medical use of classical diuretics, and new diuretic agents.
Keywords: Acetazolamide; Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors; Diuretics; Nomenclature; Pharmacological classification.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The basic groups of modern diuretic preparations. I. The mechanisms and location of the action of diuretic preparations in the nephron. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics].Ter Arkh. 1992;64(4):107-12. Ter Arkh. 1992. PMID: 1440294 Russian. No abstract available.
-
[Diuretic therapy in heart failure].Med Clin (Barc). 2014 Feb 20;142(4):163-70. doi: 10.1016/j.medcli.2013.04.027. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Med Clin (Barc). 2014. PMID: 23768854 Review. Spanish.
-
[Pharmacologic action of diuretics in the kidney].Ther Umsch. 2000 Jun;57(6):345-50. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930.57.6.345. Ther Umsch. 2000. PMID: 10894017 Review. German.
-
Site and mechanism of the action of diuretics.Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1984;54 Suppl 1:5-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1984.tb03625.x. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh). 1984. PMID: 6369884 Review.
-
[Value of aldosterone receptor blockade in diuretic therapy of patients with chronic heart failure].Herz. 2002 Mar;27(2):135-49. doi: 10.1007/s00059-002-2352-0. Herz. 2002. PMID: 12025459 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Nephrotic Syndrome: From Pathophysiology to Novel Therapeutic Approaches.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 3;12(3):569. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030569. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination diuretic therapies in heart failure: Insights from GUIDE-IT.Am Heart J Plus. 2024 Jul 30;45:100436. doi: 10.1016/j.ahjo.2024.100436. eCollection 2024 Sep. Am Heart J Plus. 2024. PMID: 39220719 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic profile, in vitro antimicrobial and in vivo diuretic effects of endemic wild thyme Thymus comosus Heuff ex. Griseb. (Lamiaceae) from Romania.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 17;14:1115117. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1115117. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36874013 Free PMC article.
-
Constituents of Chimaphila japonica and Their Diuretic Activity.Molecules. 2024 Feb 29;29(5):1092. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051092. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474601 Free PMC article.
-
Considering Adverse Effects of Common Antihypertensive Medications in the ED.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2024 Aug;26(8):355-368. doi: 10.1007/s11906-024-01304-5. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2024. PMID: 38687403 Review.
References
-
- Aktories K, Förstermann U, Hofmann FB, Starke K. Allgemeine und spezielle Pharmakologie und Toxikologie. Munich: Urban & Fischer Verlag/Elsevier GmbH; 2017.
-
- Aslam S, Gupta V (2021) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island - PubMed
-
- Brunton L, Hilal-Dandan R, Knollmann BC. Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. New York: McGraw Hill; 2017.
-
- Buckingham R. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

