Absence of endogenous carnosine synthesis does not increase protein carbonylation and advanced lipoxidation end products in brain, kidney or muscle
- PMID: 35294673
- PMCID: PMC9217836
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-022-03150-8
Absence of endogenous carnosine synthesis does not increase protein carbonylation and advanced lipoxidation end products in brain, kidney or muscle
Abstract
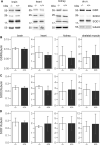
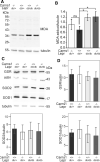
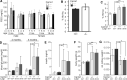
Carnosine and other histidine-containing dipeptides are expected to be important anti-oxidants in vertebrates based on various in vitro and in vivo studies with exogenously administered carnosine or its precursor β-alanine. To examine a possible anti-oxidant role of endogenous carnosine, mice lacking carnosine synthase (Carns1-/-) had been generated and were examined further in the present study. Protein carbonylation increased significantly between old (18 months) and aged (24 months) mice in brain and kidney but this was independent of the Carns1 genotype. Lipoxidation end products were not increased in 18-month-old Carns1-/- mice compared to controls. We also found no evidence for compensatory increase of anti-oxidant enzymes in Carns1-/- mice. To explore the effect of carnosine deficiency in a mouse model known to suffer from increased oxidative stress, Carns1 also was deleted in the type II diabetes model Leprdb/db mouse. In line with previous studies, malondialdehyde adducts were elevated in Leprdb/db mouse kidney, but there was no further increase by additional deficiency in Carns1. Furthermore, Leprdb/db mice lacking Carns1 were indistinguishable from conventional Leprdb/db mice with respect to fasting blood glucose and insulin levels. Taken together, Carns1 deficiency appears not to reinforce oxidative stress in old mice and there was no evidence for a compensatory upregulation of anti-oxidant enzymes. We conclude that the significance of the anti-oxidant activity of endogenously synthesized HCDs is limited in mice, suggesting that other functions of HCDs play a more important role.
Keywords: Advanced lipoxidation end products; Carnosine; Diabetes; Protein carbonylation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Carnosine synthase deficiency is compatible with normal skeletal muscle and olfactory function but causes reduced olfactory sensitivity in aging mice.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 11;295(50):17100-17113. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014188. Epub 2020 Oct 9. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33040025 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine dipeptides are key regulators of excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle: Evidence from a novel CARNS1 knockout rat model.Redox Biol. 2021 Aug;44:102016. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102016. Epub 2021 May 20. Redox Biol. 2021. PMID: 34038814 Free PMC article.
-
Carnosine synthase deficiency aggravates neuroinflammation in multiple sclerosis.Prog Neurobiol. 2023 Dec;231:102532. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2023.102532. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Prog Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37774767
-
An "enigmatic" L-carnosine (β-alanyl-L-histidine)? Cell proliferative activity as a fundamental property of a natural dipeptide inherent to traditional antioxidant, anti-aging biological activities: balancing and a hormonally correct agent, novel patented oral therapy dosage formulation for mobility, skeletal muscle power and functional performance, hypothalamic-pituitary- brain relationship in health, aging and stress studies.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2015;9(1):1-64. doi: 10.2174/1872211309666141218145408. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2015. PMID: 25524476 Review.
-
Biosynthesis of Carnosine and Related Dipeptides in Vertebrates.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018;19(8):771-789. doi: 10.2174/1389203719666180226155657. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 29484990 Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous histidine peptides are physiological antioxidants that prevent oligodendrocyte cell death and myelin loss in vivo.Glia. 2025 Jan;73(1):122-139. doi: 10.1002/glia.24624. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Glia. 2025. PMID: 39360557
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Carnosine as an Antidote against Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity and Neurotoxicity: Focus on Nrf2 Pathway.Molecules. 2022 Jul 12;27(14):4452. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144452. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review on physiological and biological activities of carnosine: turning from preclinical facts to potential clinical applications.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;398(2):1341-1366. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03427-7. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39302423 Review.
-
Anserine and Carnosine Induce HSP70-Dependent H2S Formation in Endothelial Cells and Murine Kidney.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Dec 28;12(1):66. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010066. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36670928 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Potential of Novel Carnosine Formulations: Perspectives for Drug Development.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 23;16(6):778. doi: 10.3390/ph16060778. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375726 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albrecht T, Schilperoort M, Zhang S, Braun JD, Qiu J, Rodriguez A, Pastene DO, Krämer BK, Köppel H, Baelde H, de Heer E, Anna Altomare A, Regazzoni L, Denisi A, Aldini G, van den Born J, Yard BA, Hauske SJ. Carnosine attenuates the development of both type 2 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy in BTBR ob/ob mice. Sci Rep. 2017;7:44492. doi: 10.1038/srep44492. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

