Endoplasmic reticulum-unfolded protein response pathway modulates the cellular response to mitochondrial proteotoxic stress
- PMID: 35294718
- PMCID: PMC9106787
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-022-01264-2
Endoplasmic reticulum-unfolded protein response pathway modulates the cellular response to mitochondrial proteotoxic stress
Abstract
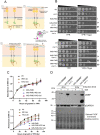
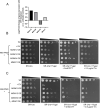
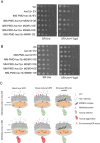
Mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) remain closely tethered by contact sites to maintain unhindered biosynthetic, metabolic, and signalling functions. Apart from its constituent proteins, contact sites localize ER-unfolded protein response (UPR) sensors like Ire1 and PERK, indicating the importance of ER-mitochondria communication during stress. In the mitochondrial sub-compartment-specific proteotoxic model of yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we show that an intact ER-UPR pathway is important in stress tolerance of mitochondrial intermembrane space (IMS) proteotoxic stress, while disrupting the pathway is beneficial during matrix stress. Deletion of IRE1 and HAC1 leads to accumulation of misfolding-prone proteins in mitochondrial IMS indicating the importance of intact ER-UPR pathway in enduring mitochondrial IMS proteotoxic stresses. Although localized proteotoxic stress within mitochondrial IMS does not induce ER-UPR, its artificial activation helps cells to better withstand the IMS proteotoxicity. Furthermore, overexpression of individual components of ER-mitochondria contact sites is found to be beneficial for general mitochondrial proteotoxic stress, in an Ire1-Hac1-independent manner.
Keywords: ER stress; ER-mitochondria contact sites; Mito-UPR; Protein homeostasis; Proteotoxic stress; Unfolded protein response.
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to [Cell Stress Society International.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sse1, Hsp110 chaperone of yeast, controls the cellular fate during endoplasmic reticulum stress.G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Jun 5;14(6):jkae075. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae075. G3 (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38577891 Free PMC article.
-
Self-association status-dependent inactivation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor Ire1 by C-terminal tagging with artificial peptides.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2022 May 24;86(6):739-746. doi: 10.1093/bbb/zbac038. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35285870
-
Ribosome depurination by ricin leads to inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced HAC1 mRNA splicing on the ribosome.J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 22;294(47):17848-17862. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009128. Epub 2019 Oct 17. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31624149 Free PMC article.
-
Translation Control of HAC1 by Regulation of Splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 12;20(12):2860. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122860. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31212749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ER Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in Leukemia: Friend, Foe, or Both?Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 30;11(2):199. doi: 10.3390/biom11020199. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33573353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic role of melatonin on acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity via reducing ER stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in a rat model.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Mar 11;26(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00900-8. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40069873 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of the p66Shc Adaptor Protein Among Mitochondrial and Mitochondria-Associated Membranes Fractions in Normal and Oxidative Stress Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 29;25(23):12835. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312835. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684546 Free PMC article.
-
TMED4 facilitates regulatory T cell suppressive function via ROS homeostasis in tumor and autoimmune mouse models.J Clin Invest. 2024 Oct 31;135(1):e179874. doi: 10.1172/JCI179874. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 39480507 Free PMC article.
-
The ER-SURF pathway uses ER-mitochondria contact sites for protein targeting to mitochondria.EMBO Rep. 2024 Apr;25(4):2071-2096. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00113-w. Epub 2024 Apr 2. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 38565738 Free PMC article.
-
Ceapin-A7 potentiates lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial injury.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Nov;37(11):e23460. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23460. Epub 2023 Jul 11. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37431958 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

