In Utero Development and Immunosurveillance of B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 35294722
- PMCID: PMC8924576
- DOI: 10.1007/s11864-022-00963-3
In Utero Development and Immunosurveillance of B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
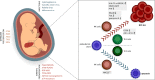
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most frequent type of pediatric cancer with a peak incidence at 2-5 years of age. ALL frequently begins in utero with the emergence of clinically silent, preleukemic cells. Underlying leukemia-predisposing germline and acquired somatic mutations define distinct ALL subtypes that vary dramatically in treatment outcomes. In addition to genetic predisposition, a second hit, which usually occurs postnatally, is required for development of overt leukemia in most ALL subtypes. An untrained, dysregulated immune response, possibly due to an abnormal response to infection, may be an important co-factor triggering the onset of leukemia. Furthermore, the involvement of natural killer (NK) cells and T helper (Th) cells in controlling the preleukemic cells has been discussed. Identifying the cell of origin of the preleukemia-initiating event might give additional insights into potential options for prevention. Modulation of the immune system to achieve prolonged immunosurveillance of the preleukemic clone that eventually dies out in later years might present a future directive. Herein, we review the concepts of prenatal origin as well as potential preventive approaches to pediatric B cell precursor (BCP) ALL.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Cancer predisposition; ETV6-RUNX1; High hyperdiploidy; Preleukemic clone; Trained immunity.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of the ETV6::RUNX1 Gene Fusion Prevalence in Newborns by Corticosteroid Use During Pregnancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 25;26(7):2971. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072971. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243620 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Insights into the prenatal origin of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020 Mar;39(1):161-171. doi: 10.1007/s10555-019-09841-1. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. PMID: 31902036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward prevention of childhood ALL by early-life immune training.Blood. 2021 Oct 21;138(16):1412-1428. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020009895. Blood. 2021. PMID: 34010407 Free PMC article.
-
ETV6/RUNX1 induces reactive oxygen species and drives the accumulation of DNA damage in B cells.Neoplasia. 2013 Nov;15(11):1292-300. doi: 10.1593/neo.131310. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 24339741 Free PMC article.
-
Functional damaging germline variants in ETV6, IKZF1, PAX5 and RUNX1 predisposing to B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Eur J Med Genet. 2023 Apr;66(4):104725. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2023.104725. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Eur J Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 36764385 Review.
Cited by
-
In Utero Origins of Acute Leukemia in Children.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 19;12(1):236. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010236. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38275407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA as a Biomarker for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Therapeutic Target in Acute and Chronic Lymphoid Leukemia.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):1979-1991. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01404-8. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 39136839 Review.
-
Early-life infection depletes preleukemic cells in a mouse model of hyperdiploid B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Blood. 2024 Aug 22;144(8):809-821. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024025038. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38875504 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA: a rising star in leukemia.PeerJ. 2023 Jul 6;11:e15577. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15577. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37431465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T cell exhaustion in pediatric B-ALL: current knowledge and future perspectives.Front Immunol. 2025 May 28;16:1531145. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1531145. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40503229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
References and Recommended Reading
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
-
- Erdmann F, Kaatsch P, Grabow D, Spix C. German Childhood Cancer Registry – Annual Report 2019 (1980-2018). Institute of Medical Biostatistics, Epidemiology and Informatics (IMBEI) at the University Medical Center of the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

