RORγt phosphorylation protects against T cell-mediated inflammation
- PMID: 35294872
- PMCID: PMC8982147
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110520
RORγt phosphorylation protects against T cell-mediated inflammation
Abstract
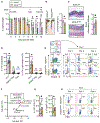
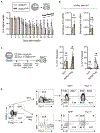
RAR-related orphan receptor-γ (RORγt) is an essential transcription factor for thymic T cell development, secondary lymphoid tissue organogenesis, and peripheral immune cell differentiation. Serine 182 phosphorylation is a major post-translational modification (PTM) on RORγt. However, the in vivo contribution of this PTM in health and disease settings is unclear. We report that this PTM is not involved in thymic T cell development and effector T cell differentiation. Instead, it is a critical regulator of inflammation downstream of IL-1β signaling and extracellular signal regulated kinases (ERKs) activation. ERKs phosphorylation of serine 182 on RORγt serves to simultaneously restrict Th17 hyperactivation and promote anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 production in RORγt+ Treg cells. Phospho-null RORγtS182A knockin mice experience exacerbated inflammation in models of colitis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). In summary, the IL-1β-ERK-RORγtS182 circuit protects against T cell-mediated inflammation and provides potential therapeutic targets to combat autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: EAE; ERK; IL-10; IL-17A; RORγt; RORγt(+) Tregs; Th17; colitis; inflammation; phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests B.S. has been a consultant to Ferring Research Institute, Gelesis, HOST Therabiomics, Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Mabwell Therapeutics, Patara Pharmaceuticals, and Takeda. The University of California, San Diego (B.S.’s institution) has received research support from Axial Biotherapeutics, BiomX, CymaBay Therapeutics, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Prodigy Biotech, and Synlogic Operating Company. B.S. is the founder of Nterica Bio.
Figures





References
-
- Abe Y, Fujiwara Y, Takahashi H, Matsumura Y, Sawada T, Jiang S, Nakaki R, Uchida A, Nagao N, Naito M, et al. (2018). Histone demethylase JMJD1A coordinates acute and chronic adaptation to cold stress via thermogenic phospho-switch. Nat. Commun 9, 1566. 10.1038/s41467-018-03868-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

