Effects of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Combined with Budesonide Treatment on Nasal Cavity Function and Serum Inflammatory Factors in Patients with Chronic Sinusitis
- PMID: 35295169
- PMCID: PMC8920662
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4140682
Effects of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Combined with Budesonide Treatment on Nasal Cavity Function and Serum Inflammatory Factors in Patients with Chronic Sinusitis
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Combined with Budesonide Treatment on Nasal Cavity Function and Serum Inflammatory Factors in Patients with Chronic Sinusitis.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9763868. doi: 10.1155/2023/9763868. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37476792 Free PMC article.
Abstract
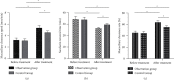
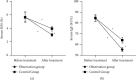
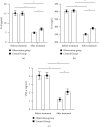
In this article, we have explored the effects of endoscopic sinus surgery together with budesonide treatment on nasal function and serum inflammatory factors on patients with chronic sinusitis. We retrospectively analyzed 120 patients with chronic sinusitis who were admitted to our hospital from March 2018 to March 2021 and were eligible for this study. They were separated into 2 groups according to different treatments, that is, the control group (treated with endoscopic surgery alone) of 58 cases and observation group (treated with endoscopic sinus surgery combined with budesonide) with 62 cases. Treatment efficacy, surgical status, overall symptom score before and after treatment, nasal mucociliary clearance function, serum eosinophils (EOS), serum immunoglobulin E (IgE), serum inflammatory factors, and occurrence of adverse reactions of both groups were recorded and compared. Total effective rate in the observation group presented strikingly more positive compared with that among patients in control group (P<0.05), as well as the data recorded in terms of operation time, blood loss during surgery and postoperative improvement time of patients (P<0.05). Overall symptom score, nasal mucociliary clearance, EOS, IgE and serum inflammatory factors in both groups were improved notably after treatment, while the observation group held a more obvious improvement. And it also had a markedly lower incidence of adverse reaction (P<0.05). Endoscopic sinus surgery combined with budesonide in the treatment of chronic sinusitis could effectively improve the clinical symptoms of patients, reestablish the function of the nasal cavity and improve their inflammation level. Meanwhile, it was of high safety and is worthy of clinical promotion.
Copyright © 2022 Yingying Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of Biyanning Granules on local symptoms and immune function of chronic rhinosinusitis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Sep;47(17):4789-4798. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220608.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36164886 Chinese.
-
Comparison of intranasal fluticasone spray, budesonide atomizer, and budesonide respules in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with polyposis after endoscopic sinus surgery.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016 Mar;6(3):233-7. doi: 10.1002/alr.21688. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016. PMID: 26679480 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of mobile phone WeChat services improve adherence to corticosteroid nasal spray treatment for chronic rhinosinusitis after functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a 3-month follow-up study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017 Mar;274(3):1477-1485. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4371-0. Epub 2016 Nov 7. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 27822702 Clinical Trial.
-
Allergy and sinusitis.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg. 1997;51(4):227-37. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg. 1997. PMID: 9444371 Review.
-
[Systematic review and Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of Biyuan Tongqiao Granules in treatment of chronic sinusitis].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Aug;47(16):4489-4504. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220512.503. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36046879 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Prelacrimal Recess Approach in Unilateral Maxillary Sinus Lesions: What Is the Impact and Efficacy?Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jan 27;60(2):222. doi: 10.3390/medicina60020222. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38399510 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Effects of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Combined with Budesonide Treatment on Nasal Cavity Function and Serum Inflammatory Factors in Patients with Chronic Sinusitis.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9763868. doi: 10.1155/2023/9763868. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37476792 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of preoperative inhaled budesonide combined with intravenous dexamethasone on postoperative sore throat in patients who underwent thyroidectomy: A randomized controlled trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 17;103(20):e38235. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038235. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38758857 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

