PET Molecular Imaging in Drug Development: The Imaging and Chemistry Perspective
- PMID: 35295604
- PMCID: PMC8919964
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.812270
PET Molecular Imaging in Drug Development: The Imaging and Chemistry Perspective
Abstract
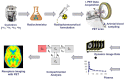
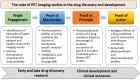
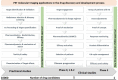
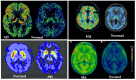
Positron emission tomography with selective radioligands advances the drug discovery and development process by revealing information about target engagement, proof of mechanism, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles. Positron emission tomography (PET) is an essential and highly significant tool to study therapeutic drug development, dose regimen, and the drug plasma concentrations of new drug candidates. Selective radioligands bring up target-specific information in several disease states including cancer, cardiovascular, and neurological conditions by quantifying various rates of biological processes with PET, which are associated with its physiological changes in living subjects, thus it reveals disease progression and also advances the clinical investigation. This study explores the major roles, applications, and advances of PET molecular imaging in drug discovery and development process with a wide range of radiochemistry as well as clinical outcomes of positron-emitting carbon-11 and fluorine-18 radiotracers.
Keywords: PET molecular imaging; carbon-11; drug development; fluorine-18; radioligands.
Copyright © 2022 Nerella, Singh, Sanam and Digwal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


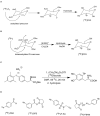
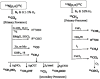
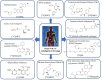
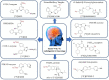
References
-
- Patel S, Schmidt K, Hesterman J, Hoppin J. Advancing drug discovery and development using molecular imaging (ADDMI): an Interest Group of the World Molecular Imaging Society and an Inaugural Session on Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Mol Imaging Biol. (2017) 19:348–56. 10.1007/s11307-017-1085-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- MEDraysintell Publishes Its New Nuclear Medicine Report and Directory. (2019). Available online at: http://medraysintell.com
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

