Acute Medication Use in Patients With Migraine Treated With Monoclonal Antibodies Acting on the CGRP Pathway: Results From a Multicenter Study and Proposal of a New Index
- PMID: 35295829
- PMCID: PMC8918478
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.846717
Acute Medication Use in Patients With Migraine Treated With Monoclonal Antibodies Acting on the CGRP Pathway: Results From a Multicenter Study and Proposal of a New Index
Abstract
Introduction: Assessing the impact of migraine preventive treatments on acute medication consumption is important in clinical evaluation. The number of acute medication intakes per each monthly migraine day (MMD) could provide insights on migraine burden and represent a new proxy of treatment effectiveness in clinical trials and real-life studies. We evaluated the effect of monoclonal antibodies acting on calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) pathway on the consumption of migraine acute medication in real-life.
Methods: In two headache centers in Prague (CZ), we included and followed up to 6 months consecutive patients treated with MoAbs acting on CGRP (erenumab or fremanezumab). For each month of treatment, we reported monthly drug intake (MDI) in doses of any medication, migraine-specific (MS), and non-migraine-specific (non-MS) medications, and computed a ratio between MMDs and MDI, i.e., Migraine Medication Index (MMI) for MS and non-MS medications.
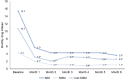
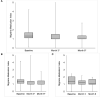
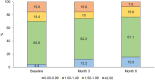
Results: We included 90 patients (91.1% women) with a median age of 47 [interquartile range (IQR) 42-51] years; 81 (90.0%) treated with erenumab and 9 (10.0%) with fremanezumab. Median MMDs decreased from 11 (IQR 8-14) at baseline to 4 (IQR 2-5) at Month 3 (p < 0.001 vs. baseline) and 3 (IQR 2-6) at Month 6 (p < 0.001 vs. baseline). Median MDI decreased from 15 drug intakes (IQR 11-20) at baseline to four drug intakes (IQR 2-7) at Month 3 (p < 0.001) and four drug intakes (IQR 2-7) at Month 6 (p < 0.001).The corresponding MDIs for MS medications were 10 (IQR 6-14) at baseline, 3 (IQR 1-5, p < 0.001) at Month 3, and 2 (IQR 0-4, p < 0.001) at Month 6. Monthly drug intakes for non-MS medications were 4 (IQR 0-9) at baseline, 1 (IQR 0-3, p < 0.001) at Month 3 and at Month 6.Median MMI decreased from 1.32 (IQR 1.11-1.68) at baseline to 1.00 (IQR 1.00-1.50, p < 0.001) at Month 3 and 1.00 (IQR 1.00-1.34, p < 0.001) at Month 6.
Conclusions: We confirmed that MoAbs acting on CGRP pathway decrease acute migraine medication consumption. We proposed a new index that can be easily applied in clinical practice to quantify migraine burden and its response to acute medication. Our index could help optimizing migraine acute treatment in clinical practice.
Keywords: calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP); medication; migraine acute treatment; monoclonal antibodies; real-life.
Copyright © 2022 Sette, Caponnetto, Ornello, Nežádal, Čtrnáctá, Šípková, Matoušová and Sacco.
Conflict of interest statement
VC had a financial relationship (lecturer or member of advisory board) with Novartis and Teva. RO has received sponsorship to attend meetings from Novartis and Teva. SS had a financial relationship (lecturer or member of advisory board) with Abbott, Allergan, Novartis, Teva, and Eli Lilly. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Steiner TJ, Stovner LJ, Jensen R, Uluduz D, Katsarava Z L L, on behalf of Lifting The Burden: the Global Campaign against Headache . Migraine remains second among the world's causes of disability, and first among young women: findings from GBD2019. J Headache Pain. (2020) 21:137. 10.1186/s10194-020-01208-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

