Baccharis dracunculifolia DC Hydroalcoholic Extract Improves Intestinal and Hippocampal Inflammation and Decreases Behavioral Changes of Colitis Mice
- PMID: 35295931
- PMCID: PMC8920628
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5833840
Baccharis dracunculifolia DC Hydroalcoholic Extract Improves Intestinal and Hippocampal Inflammation and Decreases Behavioral Changes of Colitis Mice
Abstract
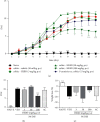
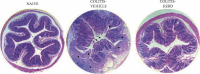
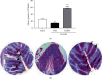
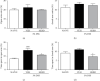
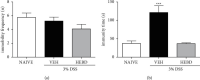
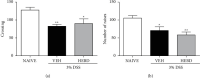
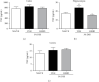
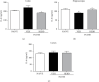
The hydroalcoholic extract of B. dracunculifolia (HEBD) and its major compound p-coumaric acid were evaluated against the severity of intestinal inflammation and behavioral changes like depressive and anxious behavior in colitis mice. Colitis was induced in Swiss mice by oral dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) administration for five days. The mice received vehicle (10 ml/kg), HEBD (3, 30, or 300 mg/kg), or p-coumaric acid (15 mg/kg) orally, once a day for twelve days. Behavioral tests were performed on the 11th and 12th days after the beginning of the treatments. Moreover, the colon, cortex, and hippocampus were collected to analyze oxidative and inflammatory parameters. The treatment with HEBD (300 mg/Kg), but not p-coumaric acid, showed decreased disease activity index (DAI) values compared to the vehicle group and partially preserved the villi architecture and mucin levels. Furthermore, the HEBD increased the antioxidant defenses in the colon and hippocampus and reduced the myeloperoxidase activity and IL-6 levels in the colon from colitis mice. Colitis mice treated with HEBD did not show depressive-like behavior in the tail suspension test. HEBD reduced colon inflammation, while it maintains antioxidant defenses and mucin levels in this tissue. It may reduce neuropsychiatric comorbidities associated with colitis through its antioxidant effects.
Copyright © 2022 Tauani Caroline Santos França et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydroalcoholic extract from Baccharis dracunculifolia recovers the gastric ulcerated tissue, and p-coumaric acid is a pivotal bioactive compound to this action.Biofactors. 2019 May;45(3):479-489. doi: 10.1002/biof.1503. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Biofactors. 2019. PMID: 30974027
-
Baccharis dracunculifolia and Brazilian green propolis extracts improve "two-hit" liver injury in MICE.Nat Prod Res. 2025 May 19:1-15. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2025.2498067. Online ahead of print. Nat Prod Res. 2025. PMID: 40388495
-
Brazilian green propolis hydroalcoholic extract reduces colon damages caused by dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice.Inflammopharmacology. 2018 Oct;26(5):1283-1292. doi: 10.1007/s10787-018-0467-z. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Inflammopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29633104
-
Hydroalcoholic extract of Tagetes erecta L. flowers, rich in the carotenoid lutein, attenuates inflammatory cytokine secretion and improves the oxidative stress in an animal model of ulcerative colitis.Nutr Res. 2019 Jun;66:95-106. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Nutr Res. 2019. PMID: 30979660
-
Canna x generalis L.H. Bailey rhizome extract ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via modulating intestinal mucosal dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and TLR4/ NF-ҡB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113670. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113670. Epub 2020 Dec 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33301917
Cited by
-
Ethnomedicinal, phytochemical and pharmacological investigations of Baccharis dracunculifolia DC. (ASTERACEAE).Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 28;13:1048688. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1048688. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36518668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrointestinal Issues in Depression, Anxiety, and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review on Pathways and Clinical Targets Implications.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(11):1371-1391. doi: 10.2174/0118715273289138240306050532. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38500273
References
-
- Teixeira F. V., Hosne R. S., Sobrado C. W. Management of ulcerative colitis: a clinical update. Journal of coloproctology . 2015;35(4):230–237. doi: 10.1016/j.jcol.2015.08.006. - DOI
-
- Maranhão D. D. A., Vieira A., Campos T. Características e diagnóstico diferencial das doenças inflamatórias intestinais. Gastroenterologia . 2015;1:9–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

