Preoperative Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) as a Superior Predictor of Long-Term Survival Outcome in Patients With Stage I-II Gastric Cancer After Radical Surgery
- PMID: 35296020
- PMCID: PMC8918673
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.829689
Preoperative Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) as a Superior Predictor of Long-Term Survival Outcome in Patients With Stage I-II Gastric Cancer After Radical Surgery
Abstract
Background: Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), calculated by immunoinflammatory cell counts of peripheral blood, is considered a predictor of survival outcome in several solid tumors, including gastric cancer (GC). However, there is no study focusing on the prognostic value of SII in the early stage of GC. This study aims to compare prognostic prediction capabilities of several inflammatory indices, nutritional indices, and tumor markers to further verify the superior prognostic value of SII in stage I-II GC patients after surgery.
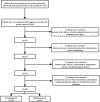
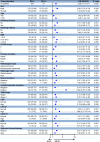
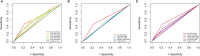
Methods: In this study, 548 patients (358 in the training group and 190 in the validation group) with stage I-II GC after radical surgery were retrospectively analyzed. The peripheral blood indices of interest were SII, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR), advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI), systemic inflammation score (SIS), prognostic nutritional index (PNI), body mass index (BMI), albumin, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), cancer antigen 125 (CA125), carbohydrate-associated antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). The time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (t-ROC) curves and the area under the curve (AUC) were used to determine the optimal cutoff value and prognostic ability of each parameter. Kaplan-Meier curves and multivariable Cox regression models were used to evaluate independent prognostic factors. The nomogram was constructed based on the result of bidirectional stepwise regression model.
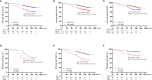
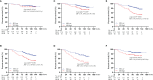
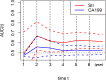
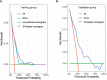
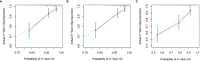
Results: The optimal cutoff value of SII was 508.3. The 5-year overall survival rate of the low SII (SII-L) group was significantly higher than that of the high SII (SII-H) group (92% vs. 80%, P < 0.001), especially in the elderly and stage II patients (91% vs. 73%, P = 0.001; 86% vs. 67%, P = 0.003, respectively). The significant prognostic values of SII were consistent in most subgroups. In multivariate analysis, SII and CA19-9 were the only two independent prognostic hematology indices. The AUC value of SII (0.624) was greater than that of CA19-9 (0.528) and other prognostic parameters. Adding SII to the conventional model improved the predictive ability of 5-year overall survival as shown by the significantly increased net reclassification improvement (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) (P = 0.033, P = 0.053, respectively) and modestly improved consistency index (C-index) (increased by 1.6%). External validation of SII-based nomogram demonstrated favorable predictive performance and discrimination. In addition, interactive web dynamic nomogram was published to facilitate clinical use.
Conclusion: SII is a simple but powerful index with a high predictive value to predict survival outcome in patients with stage I-II GC after radical operation. The SII-based nomogram can provide intuitive and accurate prognosis prediction of individual patients.
Keywords: dynamic nomogram; hematological biomarkers; inflammation indices; nutrition indices; prognosis; serum tumor markers; stage I–II gastric cancer.
Copyright © 2022 He, Si, Pan, Sun, Wang, Lu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The inflammation score predicts the prognosis of gastric cancer patients undergoing Da Vinci robot surgery.J Robot Surg. 2024 Mar 18;18(1):131. doi: 10.1007/s11701-024-01840-x. J Robot Surg. 2024. PMID: 38498240
-
[Relationship between preoperative inflammatory indexes and prognosis of patients with rectal cancer and establishment of prognostic nomogram prediction model].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022 May 23;44(5):402-409. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200630-00612. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35615796 Chinese.
-
Predicting the prognosis of patients with renal cell carcinoma based on the systemic immune inflammation index and prognostic nutritional index.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 23;14(1):25045. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76519-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39443568 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index and prognostic nutrition index in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Mar 7;18(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01631-4. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 40055764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic Review of Prognostic Role of Blood Cell Ratios in Patients with Gastric Cancer Undergoing Surgery.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Feb 25;12(3):593. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030593. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How Immunonutritional Markers Are Associated with Age, Sex, Body Mass Index and the Most Common Chronic Diseases in the Hospitalized Geriatric Population-A Cross Sectional Study.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 29;16(15):2464. doi: 10.3390/nu16152464. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39125344 Free PMC article.
-
Association between SII and hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis: A population-based study.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 15;13:925690. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.925690. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36189280 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Immune-Inflammation and Systemic Inflammation Response Indices are Predictive Markers of Mortality in Inpatients Internal Medicine Services.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Jul 26;16:3163-3170. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S420332. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37525647 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of pre-operative prognostic nutritional index and systemic immune-inflammation index for efficacy and survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Am J Transl Res. 2024 May 15;16(5):2024-2033. doi: 10.62347/RRVR5429. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38883356 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic inflammation response index predicts overall survival in patients undergoing stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer.J Radiat Res. 2025 Mar 24;66(2):129-136. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrae099. J Radiat Res. 2025. PMID: 39967449 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

