Evaluation of the impact of pre-operative stereotactic radiotherapy on the acute changes in histopathologic and immune marker profiles of brain metastases
- PMID: 35296750
- PMCID: PMC8927473
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-08507-3
Evaluation of the impact of pre-operative stereotactic radiotherapy on the acute changes in histopathologic and immune marker profiles of brain metastases
Abstract
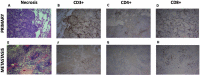
The unique acute effects of the large fractional doses that characterize stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) or radiotherapy (SRT), specifically in terms of antitumor immune cellular processes, vascular damage, tumor necrosis, and apoptosis on brain metastasis have yet to be empirically demonstrated. The objective of this study is to provide the first in-human evaluation of the acute biological effects of SRS/SRT in resected brain metastasis. Tumor samples from patients who underwent dose-escalated preoperative SRT followed by resection with available non-irradiated primary tumor tissues were retrieved from our institutional biorepository. All primary tumors and irradiated metastases were evaluated for the following parameters: tumor necrosis, T-cells, natural killer cells, vessel density, vascular endothelial growth factor, and apoptotic factors. Twenty-two patients with irradiated and resected brain metastases and paired non-irradiated primary tumor samples met inclusion criteria. Patients underwent a median preoperative SRT dose of 18 Gy (Range: 15-20 Gy) in 1 fraction, with 3 patients receiving 27-30 Gy in 3-5 fractions, followed by resection within median interval of 67.8 h (R: 18.25-160.61 h). The rate of necrosis was significantly higher in irradiated brain metastases than non-irradiated primary tumors (p < 0.001). Decreases in all immunomodulatory cell populations were found in irradiated metastases compared to primary tumors: CD3 + (p = 0.003), CD4 + (p = 0.01), and CD8 + (p = 0.01). Pre-operative SRT is associated with acute effects such as increased tumor necrosis and differences in expression of immunomodulatory factors, an effect that does not appear to be time dependent, within the limited intervals explored within the context of this analysis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R. Kotecha: Honoraria from Accuray Inc., Elekta AB, Viewray Inc., Novocure Inc., Elsevier Inc., Brainlab. Institutional research funding from Medtronic Inc., Blue Earth Diagnostics Ltd., Novocure Inc., GT Medical Technologies, Astrazeneca, Exelixis, Viewray Inc., Brainlab. R. Tonse: None. M. Menendez: None. A. Williams: None. Z. Diaz: None. M. Tom: Honoraria from Viewray Inc. Institutional research funding from Blue Earth Diagnostics Ltd. M. Hall: Honorarium from Accuray, Inc. Proton Collaborative Group Executive Committee Institutional Representative and Voting Member, Miami Cancer Institute (unpaid). Grant Funding: Live Like Bella Pediatric Cancer Research Initiative, Florida Department of Health Grant 8LA04. M.P. Mehta: Consulting for Karyopharm, Sapience, Xoft, Zap, Mevion. Board of Directors: Oncoceutics; Stock: Chimerix. R. Alvarez: None. V. Siomin: None. M. S. Ahluwalia: Receipt of grants/research supports: Astrazeneca, BMS, Bayer, Incyte, Pharmacyclics, Novocure, Mimivax, Merck. Receipt of honoraria or consultation fees: Bayer, Novocure, Kiyatec, Insightec, GSK, Xoft, Nuvation, Cellularity, SDP Oncology, Apollomics, Prelude, Janssen. Stock shareholder: Doctible, Mimivax, Cytodyn, MedInnovate Advisors LLC. Y.Odia: Institutional research funding: BMS, Novocure Inc., DSMC: GammaTile, Actuate, Oncoceutics/Chimerix. Advisory Board: Novocure Inc, Abbvie. Consulting: Abbvie. M. W. McDermott: Consulting for Deinde Medical and Stryker Corporation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of 2-staged stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases ≥ 2 cm.J Neurosurg. 2018 Aug;129(2):366-382. doi: 10.3171/2017.3.JNS162532. Epub 2017 Sep 22. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28937324
-
Single-fraction radiosurgery versus fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: a comparative study.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020 Jun;37(3):425-434. doi: 10.1007/s10585-020-10031-5. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020. PMID: 32185576
-
Resection followed by stereotactic radiosurgery to resection cavity for intracranial metastases.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 Feb 1;73(2):486-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.04.070. Epub 2008 Oct 14. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009. PMID: 18922650
-
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Postoperative Metastatic Surgical Cavities: A Critical Review and International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society (ISRS) Practice Guidelines.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Sep 1;111(1):68-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.04.016. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33891979 Review.
-
Tumor Control Probability of Radiosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 May 1;110(1):53-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.10.034. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33390244 Review.
Cited by
-
Preoperative radiosurgery for brain metastases (PREOP-1): A feasibility trial.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2024 Jun 1;47:100798. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2024.100798. eCollection 2024 Jul. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38938931 Free PMC article.
-
Update on the Management of Brain Metastasis.Neurotherapeutics. 2022 Oct;19(6):1772-1781. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01312-w. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Neurotherapeutics. 2022. PMID: 36422836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics shows that brain metastases of lung adenocarcinoma overexpress ribosomal proteins in response to gamma knife radiosurgery.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 8;14(1):15646. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58967-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38977703 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Circulating Tumor DNA as a Liquid Biomarker in Uveal Melanoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Feb 1;65(2):11. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.2.11. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38319670 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Literature and Ongoing Clinical Trials.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 4;14(17):4328. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174328. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

