A large-scaled corpus for assessing text readability
- PMID: 35297016
- PMCID: PMC10027808
- DOI: 10.3758/s13428-022-01802-x
A large-scaled corpus for assessing text readability
Abstract
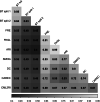
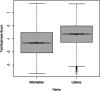
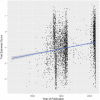
This paper introduces the CommonLit Ease of Readability (CLEAR) corpus, which provides unique readability scores for ~ 5000 text excerpts along with information about the excerpt's year of publishing, genre, and other metadata. The CLEAR corpus will provide researchers interested in discourse processing and reading with a resource from which to develop and test readability metrics and to model text readability. The CLEAR corpus includes a number of improvements in comparison to previous readability corpora including size, breadth of the excerpts available, which cover over 250 years of writing in two different genres, and unique readability criterion provided for each text based on teachers' ratings of text difficulty for student readers. This paper discusses the development of the corpus and presents reliability metrics for the human ratings of readability.
Keywords: Corpus linguistics; Natural language processing; Readability; Readability formulas.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Bailin A, Grafstein A. The linguistic assumptions underlying readability formulae: A critique. Language & Communication. 2001;21(3):285–301. doi: 10.1016/S0271-5309(01)00005-2. - DOI
-
- Best R, Floyd R, McNamara D. Differential competencies contributing to children's comprehension of narrative and expository texts. Reading Psychology. 2008;29:137–164. doi: 10.1080/02702710801963951. - DOI
-
- Biber D. Variation across speech and writing. Cambridge University Press; 1988.
-
- Bradley RA, Terry ME. Rank analysis of incomplete block designs. I. The method of paired comparisons. Biometrika. 1952;39:324–345.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

