Interpopulation variation of transposable elements of the hAT superfamily in Drosophila willistoni (Diptera: Drosophilidae): in-situ approach
- PMID: 35297941
- PMCID: PMC8961557
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2021-0287
Interpopulation variation of transposable elements of the hAT superfamily in Drosophila willistoni (Diptera: Drosophilidae): in-situ approach
Abstract
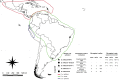
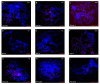
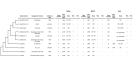
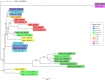
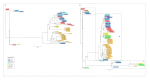
Transposable elements are abundant and dynamic part of the genome, influencing organisms in different ways through their presence or mobilization, or by acting directly on pre- and post-transcriptional regulatory regions. We compared and evaluated the presence, structure, and copy number of three hAT superfamily transposons (hobo, BuT2, and mar) in five strains of Drosophila willistoni species. These D. willistoni strains are of different geographical origins, sampled across the north-south occurrence of this species. We used sequenced clones of the hAT elements in fluorescence in-situ hybridizations in the polytene chromosomes of three strains of D. willistoni. We also analyzed the structural characteristics and number of copies of these hAT elements in the 10 currently available sequenced genomes of the willistoni group. We found that hobo, BuT2, and mar were widely distributed in D. willistoni polytene chromosomes and sequenced genomes of the willistoni group, except for mar, which is restricted to the subgroup willistoni. Furthermore, the elements hobo, BuT2, and mar have different evolutionary histories. The transposon differences among D. willistoni strains, such as variation in the number, structure, and chromosomal distribution of hAT transposons, could reflect the genomic and chromosomal plasticity of D. willistoni species in adapting to highly variable environments.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Ayala FJ, Tracey ML. Enzyme variability in the Drosophila willistoni group. J Hered. 1973;64:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Bernardo LP, Loreto ELS. hobo-brothers elements and their time and place for horizontal transfer. Genetica. 2013;141:471–478. - PubMed
-
- Bertocchi NA, de Oliveira TD, del Valle Garnero A, Coan RLB, Gunski RJ, Martins C, Torres FP. Distribution of CR1-like transposable element in woodpeckers (Aves Piciformes): Z sex chromosomes can act as a refuge for transposable elements. Chromosome Res. 2018;26:333–343. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

