Novel canine high-quality metagenome-assembled genomes, prophages and host-associated plasmids provided by long-read metagenomics together with Hi-C proximity ligation
- PMID: 35298370
- PMCID: PMC9176287
- DOI: 10.1099/mgen.0.000802
Novel canine high-quality metagenome-assembled genomes, prophages and host-associated plasmids provided by long-read metagenomics together with Hi-C proximity ligation
Abstract
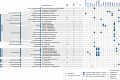
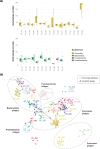
The human gut microbiome has been extensively studied, yet the canine gut microbiome is still largely unknown. The availability of high-quality genomes is essential in the fields of veterinary medicine and nutrition to unravel the biological role of key microbial members in the canine gut environment. Our aim was to evaluate nanopore long-read metagenomics and Hi-C (high-throughput chromosome conformation capture) proximity ligation to provide high-quality metagenome-assembled genomes (HQ MAGs) of the canine gut environment. By combining nanopore long-read metagenomics and Hi-C proximity ligation, we retrieved 27 HQ MAGs and 7 medium-quality MAGs of a faecal sample of a healthy dog. Canine MAGs (CanMAGs) improved genome contiguity of representatives from the animal and human MAG catalogues - short-read MAGs from public datasets - for the species they represented: they were more contiguous with complete ribosomal operons and at least 18 canonical tRNAs. Both canine-specific bacterial species and gut generalists inhabit the dog's gastrointestinal environment. Most of them belonged to Firmicutes, followed by Bacteroidota and Proteobacteria. We also assembled one Actinobacteriota and one Fusobacteriota MAG. CanMAGs harboured antimicrobial-resistance genes (ARGs) and prophages and were linked to plasmids. ARGs conferring resistance to tetracycline were most predominant within CanMAGs, followed by lincosamide and macrolide ones. At the functional level, carbohydrate transport and metabolism was the most variable within the CanMAGs, and mobilome function was abundant in some MAGs. Specifically, we assigned the mobilome functions and the associated mobile genetic elements to the bacterial host. The CanMAGs harboured 50 bacteriophages, providing novel bacterial-host information for eight viral clusters, and Hi-C proximity ligation data linked the six potential plasmids to their bacterial host. Long-read metagenomics and Hi-C proximity ligation are likely to become a comprehensive approach to HQ MAG discovery and assignment of extra-chromosomal elements to their bacterial host. This will provide essential information for studying the canine gut microbiome in veterinary medicine and animal nutrition.
Keywords: Hi-C proximity ligation; canine metagenome; gut microbiome; long-read metagenomics; metagenome-assembled genomes; nanopore.
Conflict of interest statement
A.C., N.F. and J.V. work for Vetgenomics. The other authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-read metagenomics retrieves complete single-contig bacterial genomes from canine feces.BMC Genomics. 2021 May 6;22(1):330. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07607-0. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33957869 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopore long-read-only metagenomics enables complete and high-quality genome reconstruction from mock and complex metagenomes.Microbiome. 2022 Dec 2;10(1):209. doi: 10.1186/s40168-022-01415-8. Microbiome. 2022. PMID: 36457010 Free PMC article.
-
MetaHiC phage-bacteria infection network reveals active cycling phages of the healthy human gut.Elife. 2021 Feb 26;10:e60608. doi: 10.7554/eLife.60608. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33634788 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenome-assembled genome extraction and analysis from microbiomes using KBase.Nat Protoc. 2023 Jan;18(1):208-238. doi: 10.1038/s41596-022-00747-x. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Nat Protoc. 2023. PMID: 36376589 Review.
-
Recovering metagenome-assembled genomes from shotgun metagenomic sequencing data: Methods, applications, challenges, and opportunities.Microbiol Res. 2022 Jul;260:127023. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127023. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Microbiol Res. 2022. PMID: 35430490 Review.
Cited by
-
Metagenomic assembly is the main bottleneck in the identification of mobile genetic elements.PeerJ. 2024 Jan 4;12:e16695. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16695. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38188174 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of 52 bacterial genomes from the fecal microbiome of the domestic cat (Felis catus) using Hi-C proximity ligation and shotgun metagenomics.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023 Oct 19;12(10):e0060123. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00601-23. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023. PMID: 37695121 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic community Hi-C benchmarking provides a baseline for virus-host inferences.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 23:2025.02.12.637985. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.12.637985. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39990352 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
MetaCC allows scalable and integrative analyses of both long-read and short-read metagenomic Hi-C data.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 6;14(1):6231. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41209-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37802989 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of mobile genetic elements in the ruminal microbiome of Nellore cattle.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 6;14(1):13056. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63951-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38844487 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

