Lipidomic Analysis Reveals the Protection Mechanism of GLP-1 Analogue Dulaglutide on High-Fat Diet-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice
- PMID: 35299724
- PMCID: PMC8921774
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.777395
Lipidomic Analysis Reveals the Protection Mechanism of GLP-1 Analogue Dulaglutide on High-Fat Diet-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice
Abstract
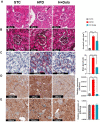
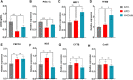
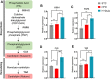
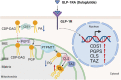
Many clinical studies have suggested that glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) have renoprotective properties by ameliorating albuminuria and increasing glomerular filtration rate in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) by lowering ectopic lipid accumulation in the kidney. However, the mechanism of GLP-1RAs was hitherto unknown. Here, we conducted an unbiased lipidomic analysis using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC/ESI-Q-TOF-MS) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) to reveal the changes of lipid composition and distribution in the kidneys of high-fat diet-fed mice after treatment with a long-acting GLP-1RA dulaglutide for 4 weeks. Treatment of dulaglutide dramatically improved hyperglycemia and albuminuria, but there was no substantial improvement in dyslipidemia and ectopic lipid accumulation in the kidney as compared with controls. Intriguingly, treatment of dulaglutide increases the level of an essential phospholipid constituent of inner mitochondrial membrane cardiolipin at the cortex region of the kidneys by inducing the expression of key cardiolipin biosynthesis enzymes. Previous studies demonstrated that lowered renal cardiolipin level impairs kidney function via mitochondrial damage. Our untargeted lipidomic analysis presents evidence for a new mechanism of how GLP-1RAs stimulate mitochondrial bioenergetics via increasing cardiolipin level and provides new insights into the therapeutic potential of GLP-1RAs in mitochondrial-related diseases.
Keywords: GLP-1R agonists; chronic kidney disease; diabetic kidney disease; dulaglutide; lipidomics; mass spectrometry imaging; obesity.
Copyright © 2022 Yeung, Leung, Choi, Yoo, Yung, So and Wong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Review of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in patients with chronic kidney disease and their renal effects.J Diabetes. 2019 Dec;11(12):938-948. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12969. Epub 2019 Aug 14. J Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 31318152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia Involvement into Acute and Chronic Brain Damage in Diabetic Rats: Impact of GLP-1RA and SGLT-2i.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Jul 24;29(7):265. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2907265. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 39082364
-
Combining glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Apr 1;22(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01798-4. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37005640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-World Effectiveness of Once-Weekly Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (OW GLP-1RAs) in Comparison with Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors (DPP-4is) for Glycemic Control and Weight Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (RELATE).Clin Drug Investig. 2024 Apr;44(4):271-284. doi: 10.1007/s40261-024-01354-2. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Clin Drug Investig. 2024. PMID: 38507188 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Clinical Outcomes to Mechanisms.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 30;11:967. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00967. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32694999 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of mitophagy in the development of chronic kidney disease.PeerJ. 2024 Apr 25;12:e17260. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17260. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38680884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potentials of Natural Antioxidants in Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 20;13(6):751. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060751. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiolipin Alterations during Obesity: Exploring Therapeutic Opportunities.Biology (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;11(11):1638. doi: 10.3390/biology11111638. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipidomic study of kidney in a mouse model with urine flow obstruction.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 5;14(1):18042. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68270-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39098953 Free PMC article.
-
Chewing the fat: How lipidomics is changing our understanding of human health and disease in 2022.Anal Sci Adv. 2023 May 10;4(3-4):104-131. doi: 10.1002/ansa.202300009. eCollection 2023 May. Anal Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38715925 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

