The Clinical Outcomes, Prognostic Factors and Nomogram Models for Primary Lung Cancer Patients Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
- PMID: 35299750
- PMCID: PMC8923348
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.863502
The Clinical Outcomes, Prognostic Factors and Nomogram Models for Primary Lung Cancer Patients Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
Abstract
Purpose: Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is a standard treatment for early primary lung cancer patients. However, there are few simple models for predicting the clinical outcomes of these patients. Our study analyzed the clinical outcomes, identified the prognostic factors, and developed prediction nomogram models for these patients.
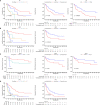
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed 114 patients with primary lung cancer treated with SBRT from 2012 to 2020 at our institutions and assessed patient's clinical outcomes and levels of toxicity. Kaplan-Meier analysis with a log-rank test was used to generate the survival curve. The cut-off values of continuous factors were calculated with the X-tile tool. Potential independent prognostic factors for clinical outcomes were explored using cox regression analysis. Nomograms for clinical outcomes prediction were established with identified factors and assessed by calibration curves.
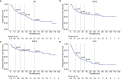
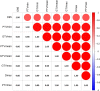
Results: The median overall survival (OS) was 40.6 months, with 3-year OS, local recurrence free survival (LRFS), distant disease-free survival (DDFS) and progression free survival (PFS) of 56.3%, 61.3%, 72.9% and 35.8%, respectively, with grade 3 or higher toxicity rate of 7%. The cox regression analysis revealed that the clinical stage, immobilization device, and the prescription dose covering 95% of the target area (D95) were independent prognostic factors associated with OS. Moreover, the clinical stage, and immobilization device were independent prognostic factors of LRFS and PFS. The smoking status, hemoglobin (Hb) and immobilization device were significant prognostic factors for DDFS. The nomograms and calibration curves incorporating the above factors indicated good predictive accuracy.
Conclusions: SBRT is effective and safe for primary lung cancer. The prognostic factors associated with OS, LRFS, DDFS and PFS are proposed, and the nomograms we proposed are suitable for clinical outcomes prediction.
Keywords: clinical outcomes; nomogram model; primary lung cancer; prognostic factors; stereotactic body radiation therapy.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Wang, Lin, Su and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Predicting 5-Year Progression and Survival Outcomes for Early Stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy: Development and Validation of Robust Prognostic Nomograms.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020 Jan 1;106(1):90-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.09.037. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020. PMID: 31586665 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Assessment of Novel Predictive Nomograms Based on APRI for Hepatitis B Virus-associated Small Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy.J Cancer. 2020 Sep 23;11(22):6642-6652. doi: 10.7150/jca.47291. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33046985 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a prognostic model for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer patients undergoing immune therapy in northernmost China and prediction of treatment efficacy based on response status at different time points.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 May 15;150(5):255. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05767-6. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38750370 Free PMC article.
-
Nomograms based on SUVmax of 18F-FDG PET/CT and clinical parameters for predicting progression-free and overall survival in patients with newly diagnosed extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma.Cancer Imaging. 2021 Jan 8;21(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00379-y. Cancer Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33419476 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of prognostic nomograms for early-onset colon cancer in different tumor locations: a population-based study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Oct 21;23(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02991-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37865754 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Signature based on RNA-binding protein-related genes for predicting prognosis and guiding therapy in non-small cell lung cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 2;13:930826. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.930826. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36118863 Free PMC article.
-
NGEF is a potential prognostic biomarker and could serve as an indicator for immunotherapy and chemotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 May 19;24(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03046-1. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38764064 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative evaluation of accumulated and planned dose deviations in patients undergoing gated and non-gated lung stereotactic body radiation therapy patients: a retrospective analysis.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 31;13(12):3616-3628. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-992. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39830749 Free PMC article.
-
A ferroptosis-related gene signature for overall survival prediction and immune infiltration in lung squamous cell carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2022 Aug 31;42(8):BSR20212835. doi: 10.1042/BSR20212835. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35866375 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of and treatment recommendations for oligometastatic disease in multidisciplinary tumor boards.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2022 Nov 15;38:123-129. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2022.11.008. eCollection 2023 Jan. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36420098 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

