Circular RNA RHOT1 Regulates miR-142-5p/CCND1 to Participate in Chondrocyte Autophagy and Proliferation in Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 35300071
- PMCID: PMC8923789
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4370873
Circular RNA RHOT1 Regulates miR-142-5p/CCND1 to Participate in Chondrocyte Autophagy and Proliferation in Osteoarthritis
Abstract
Background: Osteoarthritis (OA) serves as one of the most prevalent types of joint disorders and is a leading cause of symptoms of stiffness, swelling, and arthralgia. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been reported to participate in various cellular processes by competing with microRNAs. Meanwhile, cyclinD1 (CCND1) is a key cell cycle regulatory protein and plays a crucial role in OA progression. Nevertheless, the function of circRHOT1 in the modulation of OA progression is still obscure. Here, we explored the effect of circRHOT1 on autophagy and extracellular matrix (ECM) in OA.
Methods: The expression of circRHOT1 and autophagy markers was detected in OA samples. The effect of circRHOT1 on OA was analyzed in the OA rat model. The function of circRHOT1 in the regulation of OA was assessed by CCK-8, colony formation, flow cytometry analysis, quantitative real-time PCR, Western blot analysis, and luciferase reporter gene assay in chondrocytes.
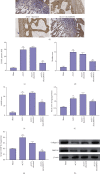
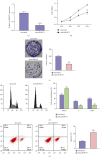
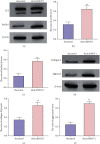
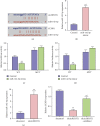
Results: We observed that autophagy markers, including LC3 and beclin1, were repressed in clinical OA samples. The expression of circRHOT1 and CCND1 was induced but the miR-142-5p expression was reduced in clinical OA samples. The miR-142-5p expression was negatively correlated with circRHOT1 and CCND1, and the circRHOT1 expression was positively associated with CCND1 in clinical OA samples. Meanwhile, the apoptosis was induced in OA rats but the depletion of circRHOT1 could block the phenotype in the rats. The articular cartilage degeneration was promoted in OA rats, while the knockdown of circRHOT1 repressed the degeneration. The serum levels of CTX-II and COMP were increased in OA rats, and the silencing of circRHOT1 downregulated levels of these proteins. In addition, the expression of collagen II and aggrecan was promoted by the depletion of circRHOT1 in the OA rats. Significantly, the expression of LC3 and beclin1 was suppressed in OA rats, in which the knockdown of circRHOT1 could reverse the effect. Moreover, the depletion of circRHOT1 repressed the cell viability and proliferation but induced apoptosis of chondrocytes. The expression levels of LC3, beclin1, collagen II, and aggrecan were induced by circRHOT1 knockdown. Mechanically, circRHOT1 was able to enhance the CCND1 expression by sponging miR-142-5p in chondrocytes. The overexpression of CCND1 or the inhibition of miR-142-5p reversed circRHOT1 depletion-mediated chondrocyte phenotypes.
Conclusions: Circular RNA RHOT1 enhances the CCND1 expression by sponging miR-142-5p to inhibit chondrocyte autophagy and promote chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis. Our findings provided a promising therapeutic target for OA.
Copyright © 2022 Gu Man et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

