User's guide to JAK inhibitors in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 35300073
- PMCID: PMC8920857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100096
User's guide to JAK inhibitors in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
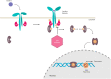
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD), are remitting and relapsing disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, highlighted by the dysregulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators, which lead to mucosal damage. These conditions cause a significant burden worldwide as primary and secondary treatment failure rates remain high even with our current therapeutic options. This emphasizes the need for continued advancement in treatment efficacy with improved safety profiles. Novel disease-targeting therapeutics have been developed, most recently being the Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi). JAKi serve as a promising new class of non-immunogenic small molecule inhibitors that modulate inflammatory pathways by blocking the critical role that Janus kinase (JAK) proteins play in mediating the innate and adaptive immune responses. Tofacitinib has been shown to be therapeutically efficacious, to have a tolerable safety profile, and to be available for adult patients with moderate-to-severe UC. This review was designed to serve as an overview and as practical guidance for medical practitioners. Author recommendations and appraisals of the quality of evidence throughout this article are based solely on personal opinion and are not the outcome of a formal methodology followed by a consensus group.
Keywords: Biologic; Efficacy; Janus kinase inhibitors; Safety; Tofacitinib; Ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Berinstein J.A., Sheehan J.l., Dias M., Berinstein E.M., Steiner C.A., Johnson L.A., Regal R.E., Allen J.I., Cushing K.C., Stidham R.W., Bishu S., Kinnucan J.A.R., Cohen-Mekelburg S.A., Waljee A.K., Higgins P.D.R. Tofacitinib for biologic-experienced hospitalized patients with acute severe ulcerative colitis: a retrospective case-control study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021;19(10):2112–2120. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chimenti M.S., Conigliaro P., Biancone L., Perricone R. Update on the therapeutic management of patients with either psoriatic arthritis or ulcerative colitis: focus on the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet Dis. 2021;13 doi: 10.1177/1759720X20977777. 1759720X20977777. Published 2021 Feb 18. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

