Characterisation of PDGF-BB:PDGFRβ signalling pathways in human brain pericytes: evidence of disruption in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 35301433
- PMCID: PMC8931009
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03180-8
Characterisation of PDGF-BB:PDGFRβ signalling pathways in human brain pericytes: evidence of disruption in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
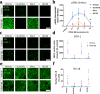
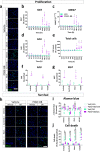
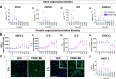
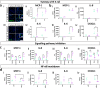
Platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB):PDGF receptor-β (PDGFRβ) signalling in brain pericytes is critical to the development, maintenance and function of a healthy blood-brain barrier (BBB). Furthermore, BBB impairment and pericyte loss in Alzheimer's disease (AD) is well documented. We found that PDGF-BB:PDGFRβ signalling components were altered in human AD brains, with a marked reduction in vascular PDGFB. We hypothesised that reduced PDGF-BB:PDGFRβ signalling in pericytes may impact on the BBB. We therefore tested the effects of PDGF-BB on primary human brain pericytes in vitro to define pathways related to BBB function. Using pharmacological inhibitors, we dissected distinct aspects of the PDGF-BB response that are controlled by extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Akt pathways. PDGF-BB promotes the proliferation of pericytes and protection from apoptosis through ERK signalling. In contrast, PDGF-BB:PDGFRβ signalling through Akt augments pericyte-derived inflammatory secretions. It may therefore be possible to supplement PDGF-BB signalling to stabilise the cerebrovasculature in AD.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
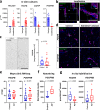

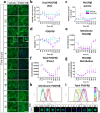
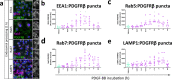
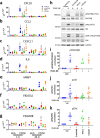
References
-
- Zlokovic BV. Neurovascular mechanisms of Alzheimer’s neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:202–208. - PubMed
-
- Yang, A. C. et al. A human brain vascular atlas reveals diverse cell mediators of Alzheimer’s disease risk. bioRxiv10.1101/2021.04.26.441262 (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

