Massively parallel enrichment of low-frequency alleles enables duplex sequencing at low depth
- PMID: 35301450
- PMCID: PMC9089460
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-022-00855-9
Massively parallel enrichment of low-frequency alleles enables duplex sequencing at low depth
Abstract
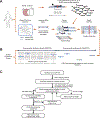
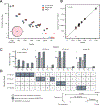
Assaying for large numbers of low-frequency mutations requires sequencing at extremely high depth and accuracy. Increasing sequencing depth aids the detection of low-frequency mutations yet limits the number of loci that can be simultaneously probed. Here we report a method for the accurate tracking of thousands of distinct mutations that requires substantially fewer reads per locus than conventional hybrid-capture duplex sequencing. The method, which we named MAESTRO (for minor-allele-enriched sequencing through recognition oligonucleotides), combines massively parallel mutation enrichment with duplex sequencing to track up to 10,000 low-frequency mutations, with up to 100-fold fewer reads per locus. We show that MAESTRO can be used to test for chimaerism by tracking donor-exclusive single-nucleotide polymorphisms in sheared genomic DNA from human cell lines, to validate whole-exome sequencing and whole-genome sequencing for the detection of mutations in breast-tumour samples from 16 patients, and to monitor the patients for minimal residual disease via the analysis of cell-free DNA from liquid biopsies. MAESTRO improves the breadth, depth, accuracy and efficiency of mutation testing by sequencing.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures

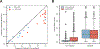

References
-
- Zahn LM Mapping genotype to phenotype. Science vol. 362 555.4–556 (2018).
-
- D’Gama AM & Walsh CA Somatic mosaicism and neurodevelopmental disease. Nat. Neurosci 21, 1504–1514 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

