Voxel-based morphometry and a deep learning model for the diagnosis of early Alzheimer's disease based on cerebral gray matter changes
- PMID: 35301516
- PMCID: PMC9890469
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhac099
Voxel-based morphometry and a deep learning model for the diagnosis of early Alzheimer's disease based on cerebral gray matter changes
Abstract
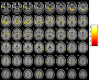
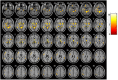
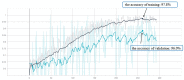
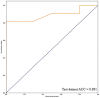
This study aimed to analyse cerebral grey matter changes in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) using voxel-based morphometry and to diagnose early Alzheimer's disease using deep learning methods based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) evaluating these changes. Participants (111 MCI, 73 normal cognition) underwent 3-T structural magnetic resonance imaging. The obtained images were assessed using voxel-based morphometry, including extraction of cerebral grey matter, analyses of statistical differences, and correlation analyses between cerebral grey matter and clinical cognitive scores in MCI. The CNN-based deep learning method was used to extract features of cerebral grey matter images. Compared to subjects with normal cognition, participants with MCI had grey matter atrophy mainly in the entorhinal cortex, frontal cortex, and bilateral frontotemporal lobes (p < 0.0001). This atrophy was significantly correlated with the decline in cognitive scores (p < 0.01). The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the CNN model for identifying participants with MCI were 80.9%, 88.9%, and 75%, respectively. The area under the curve of the model was 0.891. These findings demonstrate that research based on brain morphology can provide an effective way for the clinical, non-invasive, objective evaluation and identification of early Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: cerebral grey matter; convolutional neural network; deep learning; mild cognitive impairment; voxel-based morphometry.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Patterns of Grey Matter Atrophy at Different Stages of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's Diseases and Relation to Cognition.Brain Topogr. 2019 Jan;32(1):142-160. doi: 10.1007/s10548-018-0675-2. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Brain Topogr. 2019. PMID: 30206799
-
Structural white matter connectivity differences independent of gray matter loss in mild cognitive impairment with neuropsychiatric symptoms: Early indicators of Alzheimer's disease using network-based statistics.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024 Dec;102(4):1042-1056. doi: 10.1177/13872877241288710. Epub 2024 Nov 22. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 39574327
-
Changes of brain structure in Parkinson's disease patients with mild cognitive impairment analyzed via VBM technology.Neurosci Lett. 2017 Sep 29;658:121-132. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.08.028. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Neurosci Lett. 2017. PMID: 28823894
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
-
A review on Alzheimer's disease classification from normal controls and mild cognitive impairment using structural MR images.J Neurosci Methods. 2023 Jan 15;384:109745. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2022.109745. Epub 2022 Nov 14. J Neurosci Methods. 2023. PMID: 36395961 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of cognitive dysfunction in Parkinson's disease using voxel based morphometry and radiomics.Cogn Process. 2024 Aug;25(3):521-532. doi: 10.1007/s10339-024-01197-x. Epub 2024 May 7. Cogn Process. 2024. PMID: 38714621
-
Removing outliers from the normative database improves regional atrophy detection in single-subject voxel-based morphometry.Neuroradiology. 2024 Apr;66(4):507-519. doi: 10.1007/s00234-024-03304-3. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Neuroradiology. 2024. PMID: 38378906 Free PMC article.
-
MRI Voxel Morphometry Shows Brain Volume Changes in Breast Cancer Survivors: Implications for Treatment.Pathophysiology. 2025 Mar 12;32(1):11. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology32010011. Pathophysiology. 2025. PMID: 40137468 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Gray Matter Microstructural Alterations in Alzheimer's Disease by Free Water Imaging.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;99(4):1441-1453. doi: 10.3233/JAD-231416. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38759008 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping grey matter and cortical thickness alterations associated with subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment among rural-dwelling older adults in China: A population-based study.Neuroimage Clin. 2024;44:103691. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2024.103691. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Neuroimage Clin. 2024. PMID: 39488196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Voxel-based morphometry--the methods. NeuroImage. 2000:11(6 Pt 1):805–821. - PubMed
-
- Babikian VL, Wolfe N, Linn R, Knoefel JE, Albert ML. Cognitive changes in patients with multiple cerebral infarcts. Stroke. 1990:21(7):1013–1018. - PubMed
-
- Baron JC, Chételat G, Desgranges B, Perchey G, Landeau B, de la Sayette V, Eustache F. In vivo mapping of gray matter loss with voxel-based morphometry in mild Alzheimer's disease. NeuroImage. 2001:14(2):298–309. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Staging of Alzheimer's disease-related neurofibrillary changes. Neurobiol Aging. 1995:16(3):271–278. - PubMed
-
- Burton EJ, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Williams ED, O'Brien JT. Cerebral atrophy in Parkinson's disease with and without dementia: a comparison with Alzheimer's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and controls. Brain. 2004:127(Pt 4):791–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

