Neuroendocrine tumor secondary to pulmonary hypoplasia: A case report
- PMID: 35301802
- PMCID: PMC9013649
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.14374
Neuroendocrine tumor secondary to pulmonary hypoplasia: A case report
Abstract
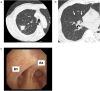
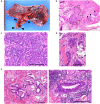
Pulmonary hypoplasia is diagnosed during the perinatal period and is a cause of death in newborns. However, these developmental abnormalities are diagnosed in adulthood in some cases. A 70-year-old male smoker was diagnosed with stage IIIA pulmonary adenocarcinoma in the right upper lobe with right middle lobe hypoplasia. He subsequently underwent right upper and middle lobectomy with lymph node dissection by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. In addition to an invasive adenocarcinoma in the right upper lobe, pathological examination of the hypoplastic lobe revealed neuroendocrine hyperplasia, as well as tumorlets and a typical carcinoid. Eight cases of pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors that developed from pulmonary hypoplasia have been reported to date. Interestingly, all but one case occurred in the right middle lobe. Neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia has been reported to develop in hypoplastic lungs postnatally; therefore, we speculated that the lesion was the origin of these neuroendocrine tumors. Moreover, the pathological findings suggested that atelectasis was involved in the pathogenesis of this rare condition. In adults, when lobar hypoplasia is diagnosed, neuroendocrine tumors should be anticipated.
Keywords: carcinoid; neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia; pulmonary hypoplasia; tumorlet.
© 2022 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Currarino G, Williams B. Causes of congenital unilateral pulmonary hypoplasia: a study of 33 cases. Pediatr Radiol. 1985;15:15–24. 10.1007/BF02387847. - PubMed
-
- Santos M, Nogueira‐Silva C, Baptista MJ, Soares‐Fernandes J, Moura RS, Correia‐Pinto J. Pulmonary epithelial cell differentiation in the nitrofen‐induced congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42:1231–7. 10.016/j.jpedsurg.2007.02.014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

