Oral Drugs Against COVID-19
- PMID: 35302484
- PMCID: PMC9400198
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.m2022.0152
Oral Drugs Against COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Five-day oral therapies against early COVID-19 infection have recently been conditionally approved in Europe. In the drug combination nirmatrelvir + ritonavir (nirmatrelvir/r), the active agent, nirmatrelvir, is made bioavailable in clinically adequate amounts by the additional administration of a potent inhibitor of its first-pass metabolism by way of cytochrome P450 [CYP] 3A in the gut and liver. In view of the central role of CYP3A in the clearance of many different kinds of drugs, and the fact that many patients with COVID-19 are taking multiple drugs to treat other conditions, it is important to assess the potential for drug interactions when nirmatrelvir/r is given, and to minimize the risks associated with such interactions.
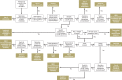
Methods: We defined the interaction profile of ritonavir on the basis of information derived from two databases (Medline, GoogleScholar), three standard electronic texts on drug interactions, and manufacturer-supplied drug information. We compiled a list of drugs and their potentially relevant interactions, developed a risk min - imization algorithm, and applied it to the substances in question. We also compiled a list of commonly prescribed drugs for which there is no risk of interaction with nirmatrelvir/r.
Results: Out of 190 drugs and drug combinations, 57 do not need any special measures when given in combination with brief, low-dose ritonavir treatment, while 15 require dose modification or a therapeutic alternative, 8 can be temporarily discontinued, 9 contraindicate ritonavir use, and 102 should preferably be combined with a different treatment.
Conclusion: We have proposed measures that are simple to carry out for the main types of drug that can interact with ritonavir. These measures can be implemented under quarantine conditions before starting a 5-day treatment with nirmatrelvir/r.
Figures
References
-
- Owen DR, Allerton CMN, Anderson AS, et al. An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science. 2021;374:1586–1593. - PubMed
-
- Mahase E. Covid-19: Pfizer’s Paxlovid is 89% effective in patients at risk of serious illness, company reports. BMJ. 2021;375 n2713. - PubMed
-
- Hsu A, Granneman GR, Bertz RJ. Ritonavir. Clinical pharmacokinetics and interactions with other anti-HIV agents. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1998;35:275–291. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

