Effector membrane translocation biosensors reveal G protein and βarrestin coupling profiles of 100 therapeutically relevant GPCRs
- PMID: 35302493
- PMCID: PMC9005190
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.74101
Effector membrane translocation biosensors reveal G protein and βarrestin coupling profiles of 100 therapeutically relevant GPCRs
Abstract
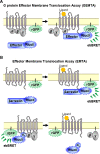
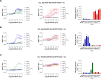
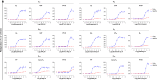
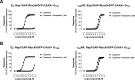
The recognition that individual GPCRs can activate multiple signaling pathways has raised the possibility of developing drugs selectively targeting therapeutically relevant ones. This requires tools to determine which G proteins and βarrestins are activated by a given receptor. Here, we present a set of BRET sensors monitoring the activation of the 12 G protein subtypes based on the translocation of their effectors to the plasma membrane (EMTA). Unlike most of the existing detection systems, EMTA does not require modification of receptors or G proteins (except for Gs). EMTA was found to be suitable for the detection of constitutive activity, inverse agonism, biased signaling and polypharmacology. Profiling of 100 therapeutically relevant human GPCRs resulted in 1500 pathway-specific concentration-response curves and revealed a great diversity of coupling profiles ranging from exquisite selectivity to broad promiscuity. Overall, this work describes unique resources for studying the complexities underlying GPCR signaling and pharmacology.
Keywords: G protein activation; biochemistry; biosensor; chemical biology; effector membrane translocation assay; enhanced bystander bioluminescence resonance energy transfer; g protein-coupled receptor; high-throughput assay; human.
© 2022, Avet et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CA, AH, SS, MC, MH, DG No competing interests declared, AM, CN, FG, SM was employee of Domain Therapeutics North America during this research, BB was employee of Domain Therapeutics North America during this research. Has filed patent application (US20200256869A1) related to the biosensors used in this work and the technology has been licensed to Domain Therapeutics, CL, HK, MH, VL has filed patent application (US20200256869A1) related to the biosensors used in this work and the technology has been licensed to Domain Therapeutics, EF, JF is employee and shares holders of Pfizer, SS, XL is employee and is part of the management of Domain Therapeutics, MB is the president of Domain Therapeutics scientific advisory board. Has filed patent application (US20200256869A1) related to the biosensors used in this work and the technology has been licensed to Domain Therapeutics
Figures


















References
-
- Aittaleb M, Nishimura A, Linder ME, Tesmer JJG. Plasma membrane association of p63 Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (p63RhoGEF) is mediated by palmitoylation and is required for basal activity in cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2011;286:34448–34456. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.273342. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armando S, Quoyer J, Lukashova V, Maiga A, Percherancier Y, Heveker N, Pin J-P, Prézeau L, Bouvier M. The chemokine CXC4 and CC2 receptors form homo- and heterooligomers that can engage their signaling G-protein effectors and betaarrestin. FASEB Journal. 2014;28:4509–4523. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-242446. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Avet C, Sturino C, Grastilleur S, Gouill CL, Semache M, Gross F, Gendron L, Bennani Y, Mancini JA, Sayegh CE, Bouvier M. The PAR2 inhibitor I-287 selectively targets Galphaq and Galpha12/13 signaling and has anti-inflammatory effects. Communications Biology. 2020;3:719. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01453-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

