Molecular Characterization of KRAS Wild-type Tumors in Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35302596
- PMCID: PMC9541577
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3581
Molecular Characterization of KRAS Wild-type Tumors in Patients with Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: KRAS mutation (MT) is a major oncogenic driver in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). A small subset of PDACs harbor KRAS wild-type (WT). We aim to characterize the molecular profiles of KRAS WT PDAC to uncover new pathogenic drivers and offer targeted treatments.
Experimental design: Tumor tissue obtained from surgical or biopsy material was subjected to next-generation DNA/RNA sequencing, microsatellite instability (MSI) and mismatch repair status determination.
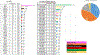
Results: Of the 2,483 patients (male 53.7%, median age 66 years) studied, 266 tumors (10.7%) were KRAS WT. The most frequently mutated gene in KRAS WT PDAC was TP53 (44.5%), followed by BRAF (13.0%). Multiple mutations within the DNA-damage repair (BRCA2, ATM, BAP1, RAD50, FANCE, PALB2), chromatin remodeling (ARID1A, PBRM1, ARID2, KMT2D, KMT2C, SMARCA4, SETD2), and cell-cycle control pathways (CDKN2A, CCND1, CCNE1) were detected frequently. There was no statistically significant difference in PD-L1 expression between KRAS WT (15.8%) and MT (17%) tumors. However, KRAS WT PDAC were more likely to be MSI-high (4.7% vs. 0.7%; P < 0.05), tumor mutational burden-high (4.5% vs. 1%; P < 0.05), and exhibit increased infiltration of CD8+ T cells, natural killer cells, and myeloid dendritic cells. KRAS WT PDACs exhibited gene fusions of BRAF (6.6%), FGFR2 (5.2%), ALK (2.6%), RET (1.3%), and NRG1 (1.3%), as well as amplification of FGF3 (3%), ERBB2 (2.2%), FGFR3 (1.8%), NTRK (1.8%), and MET (1.3%). Real-world evidence reveals a survival advantage of KRAS WT patients in overall cohorts as well as in patients treated with gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel or 5-FU/oxaliplatin.
Conclusions: KRAS WT PDAC represents 10.7% of PDAC and is enriched with targetable alterations, including immuno-oncologic markers. Identification of KRAS WT patients in clinical practice may expand therapeutic options in a clinically meaningful manner.
©2022 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests:
Philip A. Philip:
Honoraria - Array BioPharma; AstraZeneca; Bayer; Blueprint Medicines; Celgene; Ipsen; Merck; syncore; TriSalus Life Sciences
Consulting or Advisory Role - Celgene; Daiichi Sankyo; Ipsen; Merck; syncore; Taiho Pharmaceutical; TriSalus Life Sciences
Speakers’ Bureau - Bayer; Celgene; Incyte; Ipsen; Novartis
Research Funding - Advanced Accelerator Applications (Inst); ASLAN Pharmaceuticals (Inst); Bayer (Inst); boston biomedical (Inst); Caris Life Sciences (Inst); Caris Life Sciences (Inst); Genentech (Inst); halozyme (Inst); Immunomedics (Inst); incyte (Inst); incyte (Inst); Karyopharm Therapeutics (Inst); Lilly (Inst); Merck (Inst); merus (Inst); Momenta Pharmaceuticals (Inst); novartis (Inst); Plexxikon (Inst); QED Therapeutics (Inst); QED Therapeutics (Inst); Regeneron (Inst); Taiho Pharmaceutical (Inst); Taiho Pharmaceutical (Inst); TYME (Inst); tyme (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses - Abbvie; celgene; Rafael Pharmaceuticals (OPTIONAL) Uncompensated Relationships - Caris MPI; Rafael Pharmaceuticals
Ibrahim Azar: no COI.
Joanne Xiu: Employment - Caris Life Sciences
Michael J. Hall: Research Funding - Ambry Genetics; AstraZeneca; Caris Life Sciences; Foundation Medicine; InVitae; Myriad Genetics
Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property - I share a patent with several Fox Chase investigators for a novel method to investigate hereditary CRC genes (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses - AstraZeneca; Caris Life Sciences; Foundation Medicine; Myriad Genetics
Other Relationship - Caris Life Sciences; Foundation Medicine; Invitae; Myriad Genetics
Andrew Eugene Hendifar:
Consulting or Advisory Role - Abbvie; Celgene; Ipsen; Novartis; Perthera
Research Funding - Ipsen
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses - Halozyme
Emil Lou
Honoraria - Boston Scientific; Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan (Inst); GlaxoSmithKline; Novocure
Consulting or Advisory Role - Boston Scientific; Novocure; Novocure; Novocure; Novocure
Research Funding - Novocure
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses - GlaxoSmithKline
(OPTIONAL) Uncompensated Relationships - Caris Life Sciences; Minnetronix Medical; NomoCan
Jimmy J. Hwang:
Consulting or Advisory Role - Amgen; Amgen; Amgen; Amgen; Bayer; Bayer; Bayer; Bayer; Boehringer Ingelheim; Boehringer Ingelheim; Boehringer Ingelheim; Boehringer Ingelheim; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Caris Centers of Excellence; Caris Centers of Excellence; Caris Centers of Excellence; Caris Centers of Excellence; Eisai; Eisai; Eisai; Eisai; Genentech/Roche; Genentech/Roche; Genentech/Roche; Genentech/Roche; Ipsen; Ipsen; Ipsen; Ipsen;
Lilly; Lilly; Lilly; Lilly; Taiho Pharmaceutical; Taiho Pharmaceutical; Taiho Pharmaceutical; Taiho Pharmaceutical
Speakers’ Bureau - Amgen; Amgen; Amgen; Amgen; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Bristol-Myers Squibb; Celgene; Celgene; Celgene; Celgene; Genentech/Roche; Genentech/Roche; Genentech/Roche; Genentech/Roche; Ipsen; Ipsen; Ipsen; Ipsen
Research Funding - Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst); Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst); Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst); Boehringer Ingelheim (Inst); Caris Centers of Excellence (Inst); Caris Centers of Excellence (Inst); Caris Centers of Excellence (Inst); Caris Centers of Excellence (Inst)
Jun Gong:
Honoraria - Amgen; Astellas Pharma; Clinical Congress Consultants; Elsevier; Exelixis; QED Therapeutics
Consulting or Advisory Role - Amgen; Astellas Pharma; Clinical Congress Consultants; Elsevier; Exelixis; QED Therapeutics
Rebecca Feldman: Employment - Caris Life Sciences
Michelle Ellis: Employment - Caris Life Sciences
Phil Stafford: Employment - Caris Life Sciences
David Spetzler: Employment - Caris Life Sciences
Moh’d M. Khushman:
Stock and Other Ownership Interests - Aprea therapeutics; Blueprint Medicines; Daiichi Sankyo; Global Blood Therapeutics; Guardant Health; Halozyme
Speakers’ Bureau – AstraZeneca
Davendra Sohal:
Honoraria - Foundation Medicine
Consulting or Advisory Role - Ability Pharma; Perthera
Speakers’ Bureau - Incyte
Research Funding - Amgen (Inst); Apexigen (Inst); Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst); Celgene (Inst); Genentech (Inst); Incyte (Inst); Rafael Pharmaceuticals (Inst)
A. Craig Lockhart:
Research Funding - Astellas Pharma (Inst); Bristol-Myers Squibb (Inst); Merck (Inst); Sarah Cannon Research Institute (Inst)
Benjamin A. Weinberg:
Honoraria - Onclive; Rafael Pharmaceuticals; Tempus
Consulting or Advisory Role - Bayer
Speakers’ Bureau - Bayer; HalioDx; Lilly; Sirtex Medical; Taiho Pharmaceutical
Research Funding - Abbvie (Inst); Ipsen (Inst); Isofol Medical (Inst); Novartis (Inst)
Expert Testimony - AstraZeneca
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses - Boehringer Ingelheim; Caris Life Sciences
Wafik S. El-Deiry:
Stock and Other Ownership Interests - Oncoceutics; p53-Therapeutics
Consulting or Advisory Role - Boehringer Ingelheim
Research Funding - Bayer; D&D Pharmatech; D&D Pharmatech; D&D Pharmatech; Loxo; Morphotek; Tarmeta Biosciences
Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property - Patent on TIC10 (ONC201); Patents pending on the use of small molecules to target mutant p53
Other Relationship - Caris Life Sciences
John Marshall:
Employment - Caris Life Sciences; Indivumed
Honoraria - Amgen; Bayer/Onyx; Caris Life Sciences; Merck; Taiho Pharmaceutical
Consulting or Advisory Role - Amgen; Bayer/Onyx; Caris Life Sciences; Celgene; Genentech/Roche; Taiho Pharmaceutical
Speakers’ Bureau - Amgen; Bayer/Onyx; Merck; Taiho Pharmaceutical
Anthony F. Shields:
Consulting or Advisory Role - Caris Life Sciences; ImaginAb
Speakers’ Bureau - Caris Life Sciences
Research Funding - Alkermes; Astellas Pharma; AstraZeneca; Bayer; Boehringer Ingelheim; Boston Biomedical; Caris Life Sciences; Daiichi Sankyo; Eisai; Esperas Pharma; Esperas Pharma; Exelixis; Five Prime Therapeutics; H3 Biomedicine; Halozyme; Hutchison China Meditech; ImaginAb; Incyte; Inovio Pharmaceuticals; Jiangsu Alphamab Biopharmaceuticals; Lexicon; LSK BioPharma; MSK Pharma; Nouscom; Plexxikon; Repertoire Immune Medicines; Seattle Genetics; Shanghai HaiHe Pharmaceutical; Taiho Pharmaceutical; Telix Pharmaceuticals; Xencor
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses - Caris Life Sciences; GE Healthcare; ImaginAb; Inovio Pharmaceuticals; TransTarget
W. Michael Korn:
Employment - Caris Life Sciences
Leadership - Caris Life Sciences
Consulting or Advisory Role - Merck Sharp & Dohme
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses - Merck Sharp & Dohme
Figures
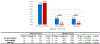


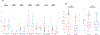
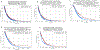
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

