The 103,200-arm acceleration dataset in the UK Biobank revealed a landscape of human sleep phenotypes
- PMID: 35302893
- PMCID: PMC8944865
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2116729119
The 103,200-arm acceleration dataset in the UK Biobank revealed a landscape of human sleep phenotypes
Abstract
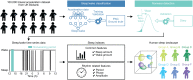
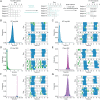
SignificanceHuman sleep phenotypes are diversified by genetic and environmental factors, and a quantitative classification of sleep phenotypes would lead to the advancement of biomedical mechanisms underlying human sleep diversity. To achieve that, a pipeline of data analysis, including a state-of-the-art sleep/wake classification algorithm, the uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) dimension reduction method, and the density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) clustering method, was applied to the 100,000-arm acceleration dataset. This revealed 16 clusters, including seven different insomnia-like phenotypes. This kind of quantitative pipeline of sleep analysis is expected to promote data-based diagnosis of sleep disorders and psychiatric disorders that tend to be complicated by sleep disorders.
Keywords: UMAP; clustering; insomnia; sleep; sleep landscape.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: M.K., S.S., K.L.O., and H.R.U. have filed a patent application regarding the sleep/wake classification algorithm. H.R.U. is the founder and Chief Technology Officer of ACCELStars Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Lander E. S., et al. ., Correction: Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 412, 565 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Venter J. C., et al. ., The sequence of the human genome. Science 291, 1304–1351 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Shendure J., et al. ., Accurate multiplex polony sequencing of an evolved bacterial genome. Science 309, 1728–1732 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

