Favourable Tolerability and Drug Survival of Tioguanine Versus Methotrexate After Failure of Conventional Thiopurines in Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 35303065
- PMCID: PMC9455785
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac044
Favourable Tolerability and Drug Survival of Tioguanine Versus Methotrexate After Failure of Conventional Thiopurines in Crohn's Disease
Abstract
Background and aims: Both methotrexate and tioguanine can be considered as treatment options in patients with Crohn's disease after failure of conventional thiopurines. This study aimed to compare tolerability and drug survival of methotrexate and tioguanine therapy after failure of conventional thiopurines in patients with Crohn's disease.
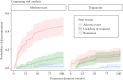
Methods: We conducted a retrospective, multicentre study, including patients with Crohn's disease initiating monotherapy methotrexate or tioguanine after failure [all causes] of conventional thiopurines. Follow-up duration was 104 weeks or until treatment discontinuation. The primary outcome was cumulative therapy discontinuation incidence due to adverse events. Secondary outcomes included total number of [serious] adverse events, and ongoing monotherapy.
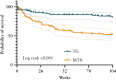
Results: In total, 219 patients starting either methotrexate [n = 105] or tioguanine [n = 114] were included. In all 65 [29.7%] patients (methotrexate 43.8% [46/105 people], tioguanine 16.7% [19/114 people], p <0.001) discontinued their treatment due to adverse events during follow-up. Median time until discontinuation due to adverse events was 16 weeks (interquartile range [IQR] 7-38, p = 0.812). Serious adverse events were not significantly different. Patients treated with methotrexate experienced adverse events more often [methotrexate 83%, tioguanine 46%, p <0.001]. Total monotherapy drug survival after 104 weeks was 22% for methotrexate and 46% for tioguanine [p <0.001].
Conclusions: We observed a higher cumulative discontinuation incidence due to adverse events for methotrexate [44%] compared with tioguanine [17%] in Crohn's disease patients after failure of conventional thiopurines. The total adverse events incidence during methotrexate use was higher, whereas serious adverse events incidence was similar. These favourable results for tioguanine treatment may guide the selection of immunosuppressive therapy after failure of conventional thiopurines.
Keywords: Inflammatory bowel diseases; immunosuppressives; side effects.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Figures
References
-
- Kozarek RA, Patterson DJ, Gelfand MD, et al. . Methotrexate induces clinical and histologic remission in patients with refractory inflammatory bowel disease. Ann Intern Med 1989;110[5]:353–6. Epub 1989/03/01. - PubMed
-
- Skinner MD, Schwartz RS.. Immunosuppressive therapy. 1. N Engl J Med 1972;287[5]:221–7. Epub 1972/08/03. - PubMed
-
- Jeuring SF, van den Heuvel TR, Liu LY, et al. . Improvements in the long-term outcome of Crohn’s disease over the past two decades and the relation to changes in medical management: results from the population-based IBDSL Cohort. Am J Gastroenterol 2017;112[2]:325–36. Epub 2016/12/07. - PubMed
-
- Torres J, Bonovas S, Doherty G, et al. . ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Medical Treatment. J Crohns Colitis 2020;14[1]:4–22. Epub 2019/11/12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical