Thoracic Involvement in Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: Pathogenesis and Management
- PMID: 35303257
- PMCID: PMC9674769
- DOI: 10.1007/s12016-022-08926-0
Thoracic Involvement in Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: Pathogenesis and Management
Abstract
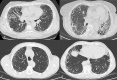
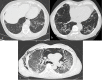
Thoracic involvement is one of the main determinants of morbidity and mortality in patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs), with different prevalence and manifestations according to the underlying disease. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is the most common pulmonary complication, particularly in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc), idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Other thoracic manifestations include pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), mostly in patients with SSc, airway disease, mainly in RA, and pleural involvement, which is common in systemic lupus erythematosus and RA, but rare in other ARDs.In this review, we summarize and critically discuss the current knowledge on thoracic involvement in ARDs, with emphasis on disease pathogenesis and management. Immunosuppression is the mainstay of therapy, particularly for ARDs-ILD, but it should be reserved to patients with clinically significant disease or at risk of progressive disease. Therefore, a thorough, multidisciplinary assessment to determine disease activity and degree of impairment is required to optimize patient management. Nevertheless, the management of thoracic involvement-particularly ILD-is challenging due to the heterogeneity of disease pathogenesis, the variety of patterns of interstitial pneumonia and the paucity of randomized controlled clinical trials of pharmacological intervention. Further studies are needed to better understand the pathogenesis of these conditions, which in turn is instrumental to the development of more efficacious therapies.
Keywords: Airways disease; Autoimmune rheumatic disorders; Connective tissue diseases; Interstitial lung disease; Pleuritis; Pulmonary arterial hypertension.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
PS reports institutional grants, personal fees and non-financial support from PPM Services and Boehringer Ingelheim, institutional grants from Roche and personal fees from Galapagos, Chiesi, Novartis, Lupin, Pieris and Santhera Pharmaceuticals, outside of the submitted work. EZ received honoraria for lectures and educational events from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Actelion and GSK. LI received honoraria for lectures and educational events from GSK. TM reports consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Roche/Genentech, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Blade Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Galapagos, Galecto, GlaxoSmithKline, IQVIA, Pliant, Respivant, Theravance and Veracyte, and honoraria for lectures or educational events from Boehringer Ingelheim and Roche/Genentech. NB received a technical consultancy contract from Chiesi. EB reports personal fees from Roche and Boehringer Ingelheim, outside the submitted work. AD received honoraria/speaking fees from GSK, Eli-Lilly, Roche, Janssen, Pfizer. All other authors declared no relevant financial or non-financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ferri C, Manfredi A, Sebastiani M, Colaci M, Giuggioli D, Vacchi C, Della Casa G, Cerri S, Torricelli P, Luppi F. Interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features and undifferentiated connective tissue disease: Our interdisciplinary rheumatology-pneumology experience, and review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev. 2016;15(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.09.003. - DOI - PubMed

