Excess neuropeptides in lung signal through endothelial cells to impair gas exchange
- PMID: 35303432
- PMCID: PMC9137452
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.02.023
Excess neuropeptides in lung signal through endothelial cells to impair gas exchange
Abstract
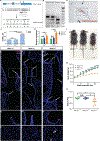
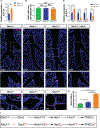
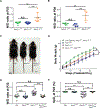
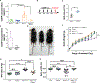
Although increased neuropeptides are often detected in lungs that exhibit respiratory distress, whether they contribute to the condition is unknown. Here, we show in a mouse model of neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia of infancy, a pediatric disease with increased pulmonary neuroendocrine cells (PNECs), excess PNEC-derived neuropeptides are responsible for pulmonary manifestations including hypoxemia. In mouse postnatal lung, prolonged signaling from elevated neuropeptides such as calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) activate receptors enriched on endothelial cells, leading to reduced cellular junction gene expression, increased endothelium permeability, excess lung fluid, and hypoxemia. Excess fluid and hypoxemia were effectively attenuated by either prevention of PNEC formation, inactivation of CGRP gene, endothelium-specific inactivation of CGRP receptor gene, or treatment with CGRP receptor antagonist. Neuropeptides were increased in human lung diseases with excess fluid such as acute respiratory distress syndrome. Our findings suggest that restricting neuropeptide function may limit fluid and improve gas exchange in these conditions.
Keywords: lung function; neuropeptides; pediatric disease; pulmonary neuroendocrine cells.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests X.S. is a member of the advisory board for Developmental Cell. J.X., L.R.Y., and X.S. have one related Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) application approved by World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) with number WO2020252368.
Figures
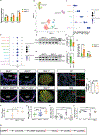

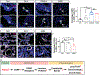
Comment in
-
The elusive pulmonary neuroendocrine cell: How rare diseases may help solving common diseases.Dev Cell. 2022 Apr 11;57(7):837-838. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.03.016. Dev Cell. 2022. PMID: 35413234
References
-
- Aiyar N, Rand K, Elshourbagy NA, Zeng Z, Adamou JE, Bergsma DJ, and Li Y (1996). A cDNA encoding the calcitonin gene-related peptide type 1 receptor. J Biol Chem 271, 11325–11329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HL148861/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL157985/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL134632/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL149741/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146141/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130938/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD023857/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL143281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL132105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026929/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070852/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG063925/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL140039/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL154926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL148436/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

