Mechanism of Borrelia immune evasion by FhbA-related proteins
- PMID: 35303742
- PMCID: PMC8967061
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010338
Mechanism of Borrelia immune evasion by FhbA-related proteins
Abstract
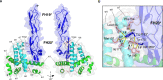
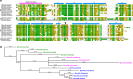
Immune evasion facilitates survival of Borrelia, leading to infections like relapsing fever and Lyme disease. Important mechanism for complement evasion is acquisition of the main host complement inhibitor, factor H (FH). By determining the 2.2 Å crystal structure of Factor H binding protein A (FhbA) from Borrelia hermsii in complex with FH domains 19-20, combined with extensive mutagenesis, we identified the structural mechanism by which B. hermsii utilizes FhbA in immune evasion. Moreover, structure-guided sequence database analysis identified a new family of FhbA-related immune evasion molecules from Lyme disease and relapsing fever Borrelia. Conserved FH-binding mechanism within the FhbA-family was verified by analysis of a novel FH-binding protein from B. duttonii. By sequence analysis, we were able to group FH-binding proteins of Borrelia into four distinct phyletic types and identified novel putative FH-binding proteins. The conserved FH-binding mechanism of the FhbA-related proteins could aid in developing new approaches to inhibit virulence and complement resistance in Borrelia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Borrelia hermsii factor H binding protein FhbA is not required for infectivity in mice or for resistance to human complement in vitro.Infect Immun. 2014 Aug;82(8):3324-32. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01892-14. Epub 2014 May 27. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24866803 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analyses of the interaction of Borrelia hermsii FhbA with the complement regulatory proteins factor H and factor H-like protein 1.Infect Immun. 2006 Apr;74(4):2007-14. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.4.2007-2014.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16552029 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological and molecular analyses of the Borrelia hermsii factor H and factor H-like protein 1 binding protein, FhbA: demonstration of its utility as a diagnostic marker and epidemiological tool for tick-borne relapsing fever.Infect Immun. 2006 Aug;74(8):4519-29. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00377-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16861638 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Evasion Strategies of Relapsing Fever Spirochetes.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 23;11:1560. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01560. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32793216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complement evasion strategies of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato.FEBS Lett. 2020 Aug;594(16):2645-2656. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13894. Epub 2020 Aug 11. FEBS Lett. 2020. PMID: 32748966 Review.
Cited by
-
The life-and-death struggle between the complement system and pathogens: Mechanisms of elimination, evasion tactics, and translational potential.Virulence. 2025 Dec;16(1):2553781. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2553781. Epub 2025 Sep 4. Virulence. 2025. PMID: 40905313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The human factor H protein family - an update.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 12;15:1135490. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1135490. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38410512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production, purification, and quality assessment of borrelial proteins CspZ from Borrelia burgdorferi and FhbA from Borrelia hermsii.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 23;108(1):425. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13195-2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39042328 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbosa A.S., I L. Complement Immune Evasion by Spirochetes in Spirochete Biology: The Post Genomic Era. A B., editor: Springer, Cham; 2017.
-
- Adeolu M, Gupta RS. A phylogenomic and molecular marker based proposal for the division of the genus Borrelia into two genera: the emended genus Borrelia containing only the members of the relapsing fever Borrelia, and the genus Borreliella gen. nov. containing the members of the Lyme disease Borrelia (Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex). Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2014;105(6):1049–72. doi: 10.1007/s10482-014-0164-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rizzoli A, Hauffe H, Carpi G, Vourc HG, Neteler M, Rosa R. Lyme borreliosis in Europe. Euro Surveill. 2011;16(27). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

