Hemoptysis due to progressive scoliosis associated with congenital heart disease: a case report
- PMID: 35303835
- PMCID: PMC8932114
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05225-9
Hemoptysis due to progressive scoliosis associated with congenital heart disease: a case report
Abstract
Background: Patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) are associated with an increased incidence of scoliosis, often with severe progression. We report a case of hemoptysis caused by rapid scoliosis progression subsequent to surgery for CHD that was successfully managed by surgical curve correction following coil embolization.
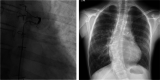
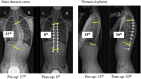
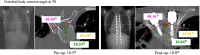
Case presentation: A 14-year-old girl with scoliosis had undergone open heart surgery for CHD at the age of 1 year. She was first noted to have scoliosis at 12 years of age, which began to progress rapidly. At age 13, her main thoracic curve Cobb angle was 46°, and hemoptysis with high pulmonary vein pressure due to vertebral rotation was detected. Nine months after coil embolization, she received posterior spinal fusion from T5 to L2 for scoliosis correction. Postoperatively, her pulmonary vein diameter was enlarged, with no detectable signs of hemoptysis.
Conclusions: We encountered a case of hemoptysis caused by advanced scoliosis after cardiac surgery that was successfully treated by correction of the scoliotic curve following coil embolization. Patients with secondary scoliosis after surgery for CHD should be carefully monitored for the possibility of cardiovascular system deterioration.
Keywords: Congenital heart disease; Hemoptysis; Pulmonary vein stenosis; Scoliosis; Spinal correction.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or other conflicts or interest in relation to this research and its publication. Masashi Uehara is a member of the editorial board of this journal.
Figures



References
-
- Niebauer JJ, Wright WD. Congenital heart disease and scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1956;38-A:1131–1136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

