An update on the clinical approach to giant cell arteritis
- PMID: 35304369
- PMCID: PMC8966809
- DOI: 10.7861/clinmed.2022-0041
An update on the clinical approach to giant cell arteritis
Abstract
Recent national and international guidance from rheumatology societies have reflected the advances in evidence for both the investigation and management of giant cell arteritis. Cranial ultrasound reduces diagnostic delay and improves clinical outcomes. Immediate high-dose glucocorticoids remain the standard treatment for giant cell arteritis. Randomised controlled trial evidence using tocilizumab, an interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, has been shown to have good clinical efficacy with glucocorticoid sparing effects. Overall patient outcomes appear to be improved by formalising pathways for diagnosis to include clinical experts' opinion early in decision making.
Keywords: giant cell arteritis; temporal arteritis; temporal artery biopsy; tocilizumab; ultrasound.
© Royal College of Physicians 2022. All rights reserved.
Figures
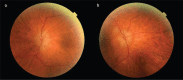
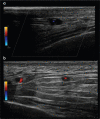
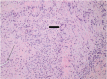

References
-
- Kaushik M, Ponte C, Mollan SP. Current advances in giant cell arteritis. Curr Opin Neurol 2021;34;133–41. - PubMed
-
- Kønig EB, Stormly Hansen M, Foldager J, et al. . Seasonal variation in biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis in Eastern Denmark from 1990-2018. Acta Ophthalmol 2021;99;527–32. - PubMed
-
- Hellmich B, Agueda A, Monti S, et al. . 2018 Update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of large vessel vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79;19–30. - PubMed
-
- Mackie SL, Dejaco C, Appenzeller S, et al. . British Society for Rheumatology guideline on diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2020;59;e1–23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

