Aged bone matrix-derived extracellular vesicles as a messenger for calcification paradox
- PMID: 35304471
- PMCID: PMC8933454
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29191-x
Aged bone matrix-derived extracellular vesicles as a messenger for calcification paradox
Abstract
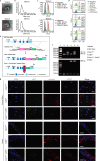
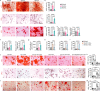
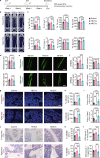
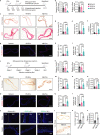
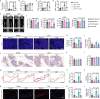
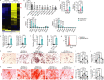
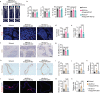
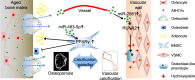
Adipocyte differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (BMSCs) instead of osteoblast formation contributes to age- and menopause-related marrow adiposity and osteoporosis. Vascular calcification often occurs with osteoporosis, a contradictory association called "calcification paradox". Here we show that extracellular vesicles derived from aged bone matrix (AB-EVs) during bone resorption favor BMSC adipogenesis rather than osteogenesis and augment calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. Intravenous or intramedullary injection of AB-EVs promotes bone-fat imbalance and exacerbates Vitamin D3 (VD3)-induced vascular calcification in young or old mice. Alendronate (ALE), a bone resorption inhibitor, down-regulates AB-EVs release and attenuates aging- and ovariectomy-induced bone-fat imbalance. In the VD3-treated aged mice, ALE suppresses the ovariectomy-induced aggravation of vascular calcification. MiR-483-5p and miR-2861 are enriched in AB-EVs and essential for the AB-EVs-induced bone-fat imbalance and exacerbation of vascular calcification. Our study uncovers the role of AB-EVs as a messenger for calcification paradox by transferring miR-483-5p and miR-2861.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gu W, et al. Role of NFATc1 in the Bone-Vascular Axis Calcification Paradox. J. Cardiovasc Pharm. 2020;75:200–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

